UFC 3-280-03
23 JULY 2003
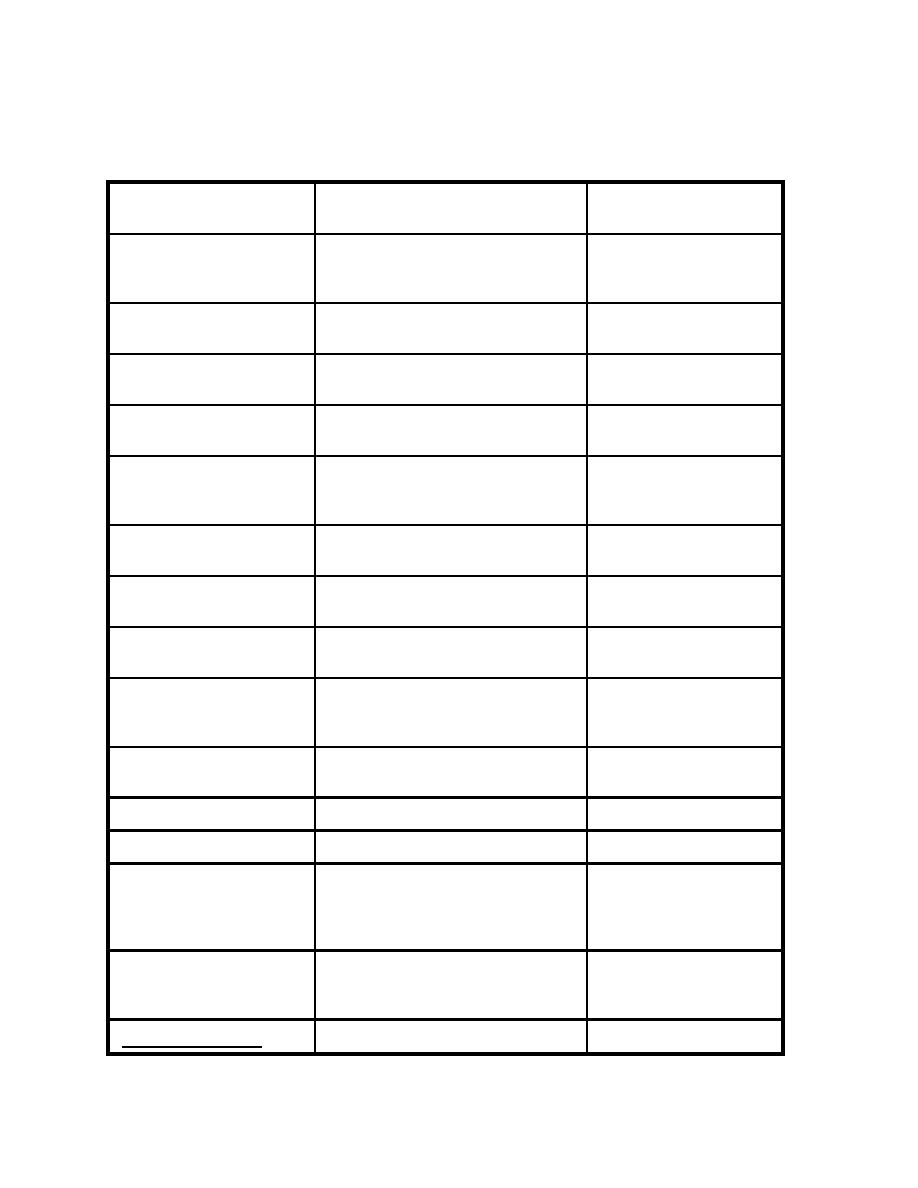
Table 2-6. Overview of typical design conditions for filter press applications.
Parameter1,2
Applicability
Typical Design
Conditions2
Sludge Type/
Specific to source of generation.
Characteristics (Paragraph
3.1)
Sludge Storage (Paragraph
As required.
4 days' minimum, typical.
4.2)
Sludge Transport
(Paragraph 4.3)
Feed Pump Type:
See Table 2-7 for general selection
Application specific.
guide.
Feed Pump Pressure:
Application specific to sludge and types
See Tables 2-4 and 2-5 for
of press used.
typical pressure
applications.
-Low-Pressure Unit
Fixed-volume press only.
350860 kPa
(690 kPa terminal)
-High-Pressure Unit
Fixed-volume press only.
10401730 kPa
(1550 kPa terminal)
-Fast Press Filling
Variable-volume press only.
350860 kPa
(Up to 690 kPa)
Variable-volume press only, using water
5501730 kPa
-Membrane Water
as membrane inflation media.
Inflation
(Up to 1550 kPa)
Feed pressure stepping
Either type of press.
intervals:
-
Low-Pressure Unit
180 kPa
-
High-Pressure Unit
350520 kPa
Sludge Pretreatment
Specific requirements
See Tables 2-4 and 2-5 for typical
based on treatability
(Paragraph 2-4.4)
conditioning requirements for both types
studies (Paragraph 2-6).
of presses for various sludge
applications.
Major Filter Press
Components
(Paragraph 2-4.5)
Essential Components:
Required for either type of press.
2-26



 Previous Page
Previous Page
