TM 5-814-7
CHAPTER 5
LAND DISPOSAL/LAND TREATMENT OPTIONS
included in this chapter for each disposal option under
5-1. Introduction
the section on Design Elements. Closure standards,
a. This chapter of the manual presents a general
mandated by 40 CFR 264, subpart G, are designed to
discussion of landfills, surface impoundments, land
extend protection of human health and the environment
treatment, deep well injection and waste piles with
beyond the active life of a facility.
respect to:
e. As defined by RCRA, each of the disposal
Wastes Suitable for Disposal
options has characteristics that distinguishes it from the
Limitations of Each Disposal Option
others; however, as noted below, some overlapping in
Disposal Procedures
definition
occurs
with
landfills
and
surface
Design Elements
impoundments. The RCRA definitions of these five
Equipment
disposal options are summarized below.
b. The treatment of each of these topics is brief,
(1) A landfill is defined in 40 CFR 260.10 as a
focusing on the needs of the design engineer. Where
disposal facility or part of a facility where hazardous
appropriate, reference has been made to source
waste in bulk or containerized form is placed in or on
documents for additional information on these topics.
land, typically in excavated trenches or cells. However,
With respect to design elements, this chapter
DA hazardous waste landfills must not accept bulk
summarizes the elements required for each of the five
liquids or sludges with leachable liquids.
disposal options at Army installations. Since these
(2) A surface impoundment, according to 40
elements constitute the key design tools for meeting
CFR 262.10, is a facility (or part of a facility) that is a
RCRA requirements for hazardous waste land
natural topographic depression, man-made excavation,
treatment/disposal facilities, they are treated in detail in
or diked area formed primarily of earthen materials
chapter 6.
(although it may be lined with man-made materials)
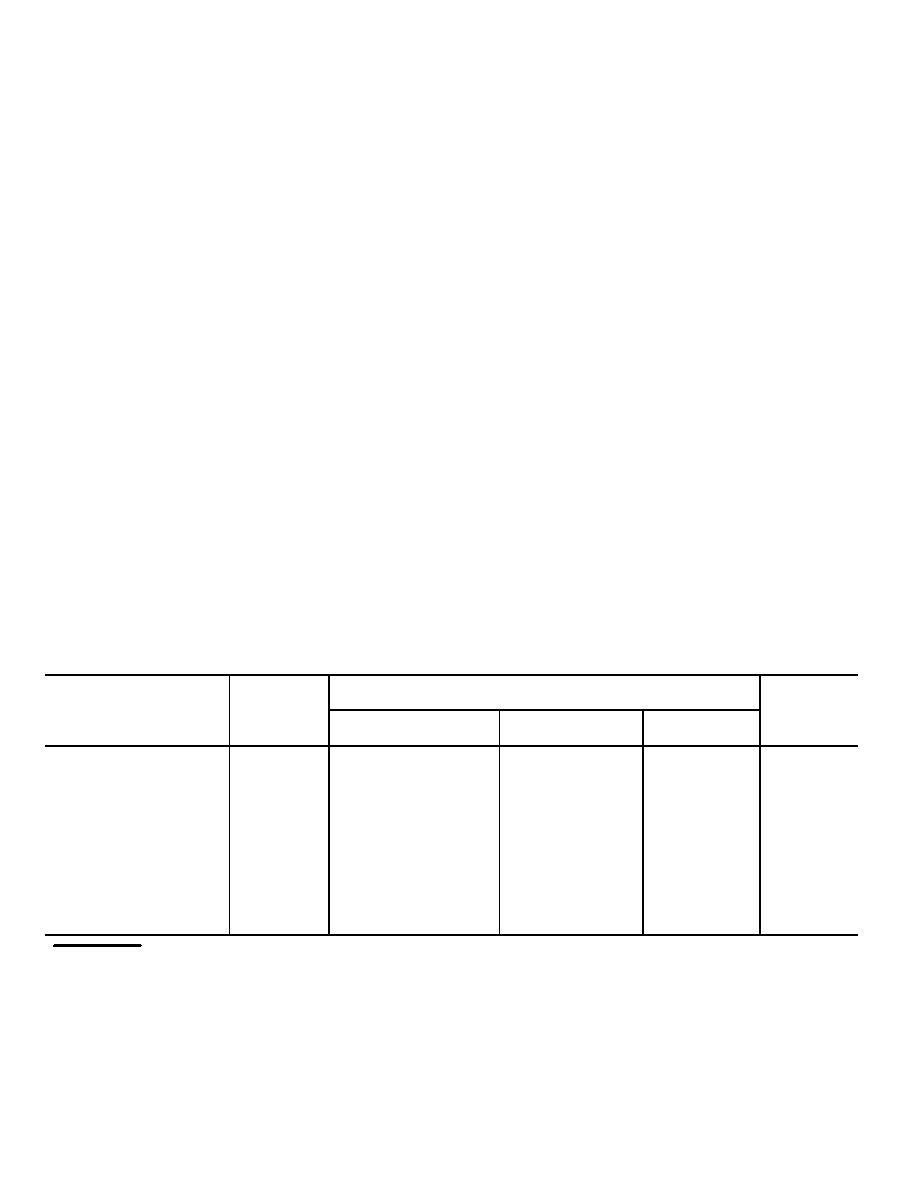
c. Table 5-1 lists the design elements required for
designed to hold an accumulation of liquid wastes or
DA land disposal/land treatment facilities and refers to
wastes containing free liquid. According to this definition,
the sections of the manual where these are discussed in
a surface impoundment is assumed to have a fluid
detail. Figure 5-1 presents a conceptual layout of a
surface and hold non-containerized free bulk liquids.
hazardous waste facility master plan with landfill, surface
Examples of surface impoundments are holding,
impoundment, land treatment, and waste pile units.
storage, settling, and aeration pits, ponds, and lagoons.
d. The design engineer should be familiar with
Surface impoundments can be classified as disposal,
closure requirements for a given unit; therefore, these
storage
or
treatment
facilities,
as
follows:
are
Table 5-1. Design Features Required by RCRA
a
For DA Land Disposal/land Treatment Facilities
Disposal/Land Treatment Facilities
b
Facility Elements
Reference
Surface
Waste Piles
Land
Landfills
Impoundments
Treatment
Liner System C
6-3
Required
Required
NA
Required
Leak Detection System
6-4
Required
Required
NA
Required
Monitoring Wells
8-3
Required
Required
Required
Required
Leachate Collection and
6-4
NA
Required
NA
Required
Removal Systems
Run-on/Run-off Controls
6-5
Required
Required
Required
Required
Wind Dispersal Controls
6-8
NA
Required
Required
Required
Overtopping Controls
6-8
Required
NA
NA
NA
Cap (Final Cover)
6-7
Required (disposal)
NA
NA
Required
Closure and Post-
5-2, 5-3,
Required (disposal)
NA
Required
Required
Closure Care
5-4
a
Injection wells are excluded from this table since their design features are unique. See paragraph 5-5 of this manual.
b
Paragraph(s) in this TM describing the design feature.
c
Double liners are required at all DA installations unless a waiver is obtained from HQ, (DAEN-ECE-G), Washington, DC
20314
US Army Corps of Engineers.
5-1



 Previous Page
Previous Page
