TM 5-623
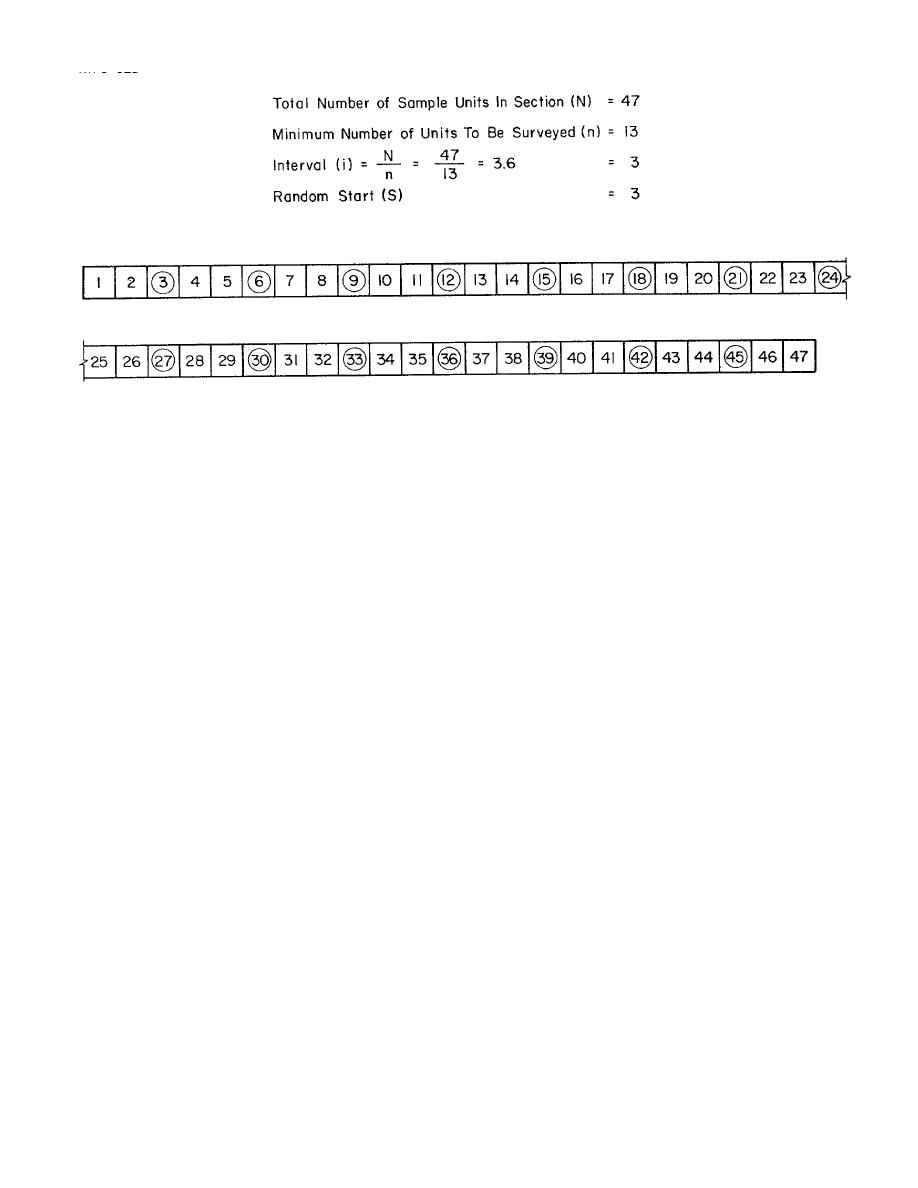
Figure 3-5. Example selection of sample units to be surveyed.
(1) The "sampling interval" (i) is determined
was not selected at random and/or contains distress(es)
by i=N/n, where N=total number of available sample
which are not representative of the section.
(2) The calculation of the PCI when additional
units, n=minimum
number of sample units to be
sample units are included is slightly altered and its
surveyed, and i is rounded off to the smaller whole
described in paragraph 3-5.
number (e.g., 3.6 is rounded to 3).
(2) The random start (s) is selected at random
3-5. Calculating the PCI from inspection results
between 1 and the sampling interval (i). For example, if
a. General. Paragraph 3-4 described two ways of
i=3, the random start would be a number from 1 to 3.
inspecting a pavement section; i.e., inspecting every unit
(3) The sample units to be surveyed are
in the section or inspecting by sampling. Data collected
identified as s, s+i, s+2i, s+3i, etc. If the selected start is
during either method of inspection are used to calculate
3, then the samples to be surveyed are 3, 6, 9, 12, etc.
the PCI. This paragraph explains how to calculate the
(See fig 3-5.) This technique is simple to apply and also
PCI for a particular sample unit, and how to calculate the
gives the information necessary to establish a PCI profile
PCI for the entire pavement section. An important item
along the pavement section.
in the calculation of the PCI is the "deduct value." A
d. Selection of additional sample units. One of the
deduct value is a number from 0 to 100, with 0 indicating
major objections to sampling is the problem of not
the distress has no impact on pavement condition, and
including very "poor" or "excellent" sample units which
100 indicating an extremely serious distress which
may exist in a section. Another problem is the selection
causes the pavement to fail.
of a random sample which contains nontypical distresses
b. Calculating sample unit PCI. Calculating the PCI
such a railroad crossings, potholes, etc.
for a sample unit is a simple procedure which involves
(1) To overcome these problems, the
five steps (see fig 3-6):
inspector should label unusual sample units as additional
sample units. An additional unit implies that the sample
3-6



 Previous Page
Previous Page
