TM 5-018-7
(B-9)
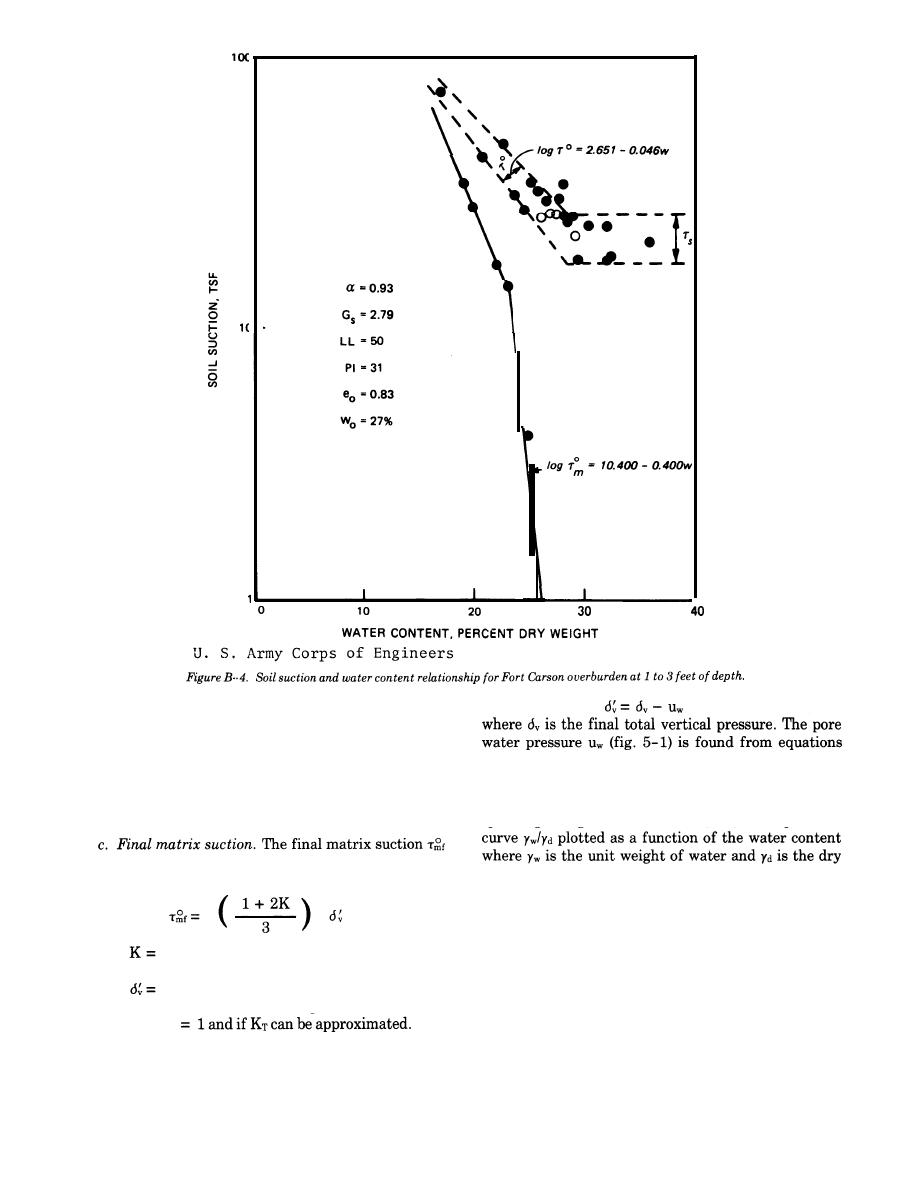
if the equilibrium moisture profiles of figure 5-1 (para
5-4b) are used.
b. Initial matrix suction. The initial matrix suction
(5-3), (5-4), or (5-5).
surcharge pressure may be evaluated using
T&without
d. Compressibility factor. The compressibility fac-
the soil suction test procedure on undisturbed speci-
tor a is the ratio of the change in volume for a corre-
mens or may be calculated from equation (B-7) and
sponding change in water content, i.e., the slope of the
the natural (initial) water content.
without surcharge pressure may be calculated from
density. The value of a for highly plastic soils is close
the assumption
to 1, and much less than 1 for sandy and low plasticity
soils. High compressibility y factors can indicate highly
(B-8)
swelling soils; however, soils with all voids filled with
water also have a equal to 1.
coefficient of effective lateral earth pres-
(1) Figure B-5 illustrates the compressibility fac-
sure
tor calculated from laboratory data for a silty clay
final vertical effective pressure, tons per
taken from a field test section near Clinton, Missis-
square foot or from equation (B-1) setting
sippi. Extrapolating the line to zero water content, as
a
shown in the figure, provides an estimate of l/R with
The final vertical effective pressure may be found
from
B-7



 Previous Page
Previous Page
