CEMP-ET
TI 809-53
01 May 1999
wool batts, blown loose insulations such as cellulose fiber, glass fiber, mineral fiber, and
expanded vermiculite. Table 2-11 indicates suitability of rigid roof insulations for membrane
roofing based upon intended method of use.
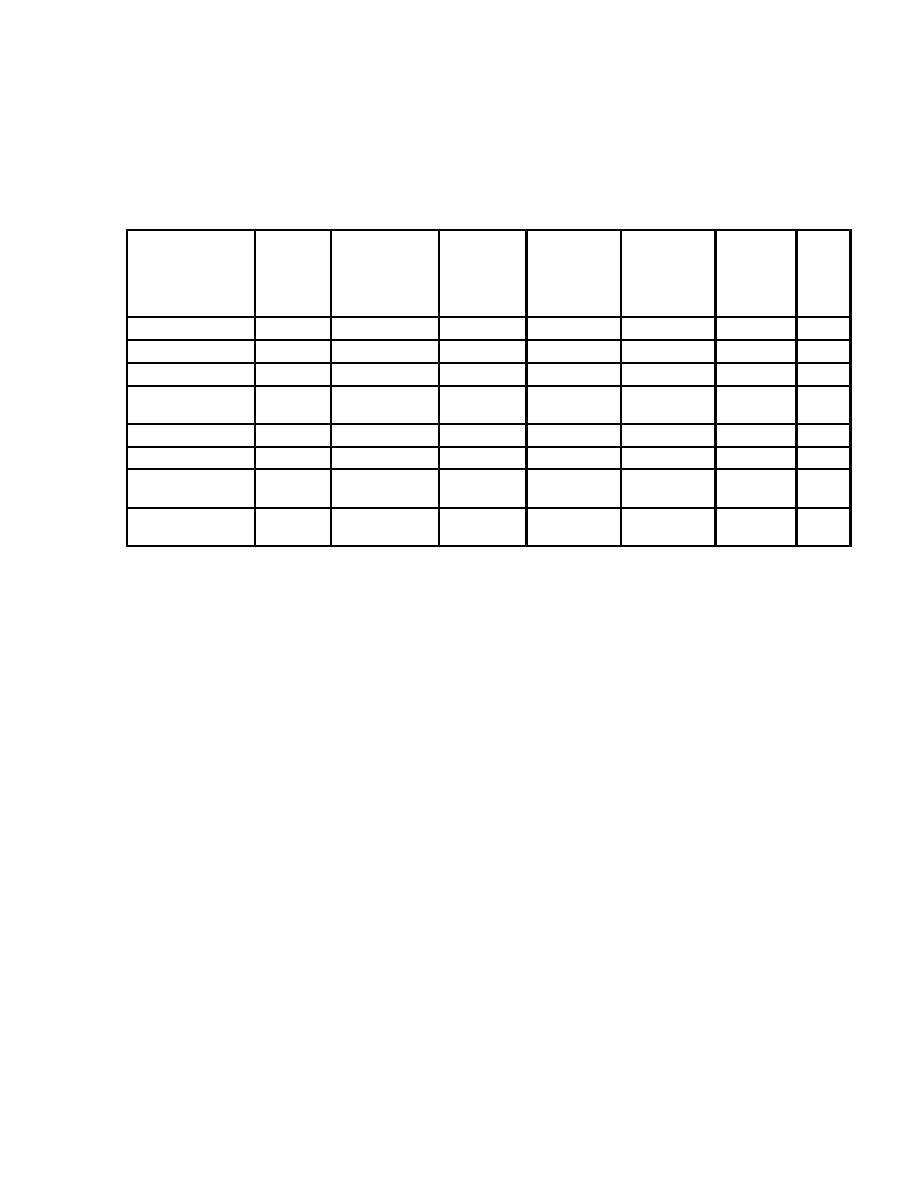
Table 2-11. Suitability of Roof Insulation for Method of Use
Direct
Mechanical
Solvent
High
Fire
Asphalt
Use
Attach-
Attachment
Adhesive
Thermal
Resistant
Compat-
in
ment to
Value/Unit
ible
PMR
Steel
Thickness
Decks
Wood Fiber
(a)
Yes
Yes
No
No
Yes
No
Perlite Fiber
Yes
Yes
(b)
No
Yes
Yes
No
Glass Fiber
Yes
(f)
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
No
Polystyrene
(c)
(d)
No
Yes
No
No
No
MEPS
Polystyrene XEPS
(c)
(d)
No
Yes
No
No
Yes
Polyisocyanurate
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
(e)
No
Foam
Glass
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
No
Board
Mineral
Wool
Yes
(f)
No
No
Yes
Yes
No
Fiber
(a) Wood fiber is available with <4% asphalt to meet under-deck fire requirements for steel decks.
(b) Asphaltic adhesives are permitted to attach membranes to perlite boards, but not single-ply
adhesives.
(c) Some polystyrene applications have passed fire testing when used in conjunction with single-ply
systems only. It is not universally agreed that this is an acceptable application.
(d) Mechanical fasteners compress polystyrene insulation, resulting in loss of restraining force.
Overlay with rigid board such as perlite.
(e) Overlay with non-foam layer for hot BUR or MB application.
(f) Special stress plates needed to recess heads of screws.
(1) Thickness of Insulation. If thick layers of insulation are needed to meet a high therm
resistance, thicker wood nailers and deeper fascia metal will be required. Foam plastics such
as polyisocyanurate and polystyrene have the highest R values per unit thickness.
(2)
Clearance of Metal Panels. In standing seam metal roof systems, the
permissible thickness of blanket insulation may be limited by the clearance provided by the
supporting clip design.
(3)
Insulated Attic. Blanket insulation used in steep roofing systems is frequently
placed on the floor of the attic where R-values of 30 (RSI = 5.4) or more may be possible (figure
2-13).
(4)
Ceiling Insulation. Dropped ceilings are sometimes insulated by placing batts
directly above the ceiling panels. This practice is not recommended as subsequent access to
underdeck equipment or phone wires is blocked. When the insulation is displaced to gain access
it is rarely put back in place correctly, if at all.
h. Suitability for Extreme Climates. Protected membrane systems (PMRs) are very well
suited to extremely cold climates and have been successfully used in all climates. For extreme
conditions of snow and ice, a cold (ventilated) roof should be considered. For most steep roofing
2-13



 Previous Page
Previous Page
