CEMP-E
TI 809-07
NOVEMBER 1998
(1) Section A, General Provisions. This section discusses the limits of applicability,
materials, loads allowable stress design (ASD), load resistance factor design (LRFD), strength
increase due to cold working, and serviceability.
(2) Section B, Elements. This section discusses dimensional limits, the effective
widths of stiffened and unstiffened elements, and stiffeners. This analysis considers the flat
widths and thickness of the flange, the web, and the lip, along with the effects of any intermediate
stiffeners. The element analysis is used to determine the effectiveness of the element and the
design stress level for that element.
(3) Section C, Members. This section goes into the calculation of section properties,
the design of tension members, flexural members, concentrically loaded members, members in
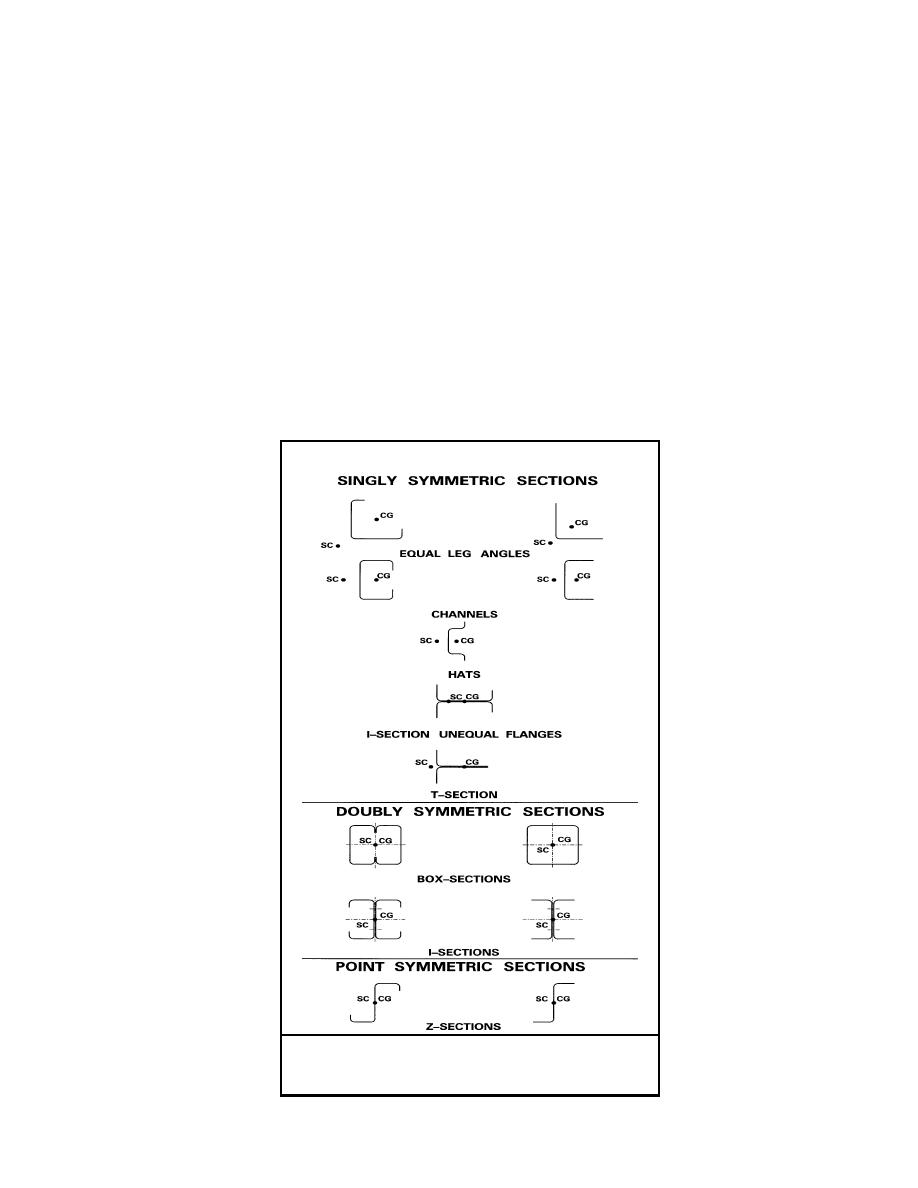
combined axial and bending, and cylindrical tubular members. In Figure 2-1 is shown the
common section symmetries used in cold-formed steel design. Section symmetries are defined
by using the relative positions of the center of gravity (CG) and shear center (SC) of the sections
geometry. Sections having separate locations for the CG and SC are singly symmetric. When
they are collocated at the same point they are doubly or point (Z sections of equal flange width)
symmetric.
Figure 2-1 Typical Cold-Formed Section Symmetries
2-3



 Previous Page
Previous Page
