TM 5-623
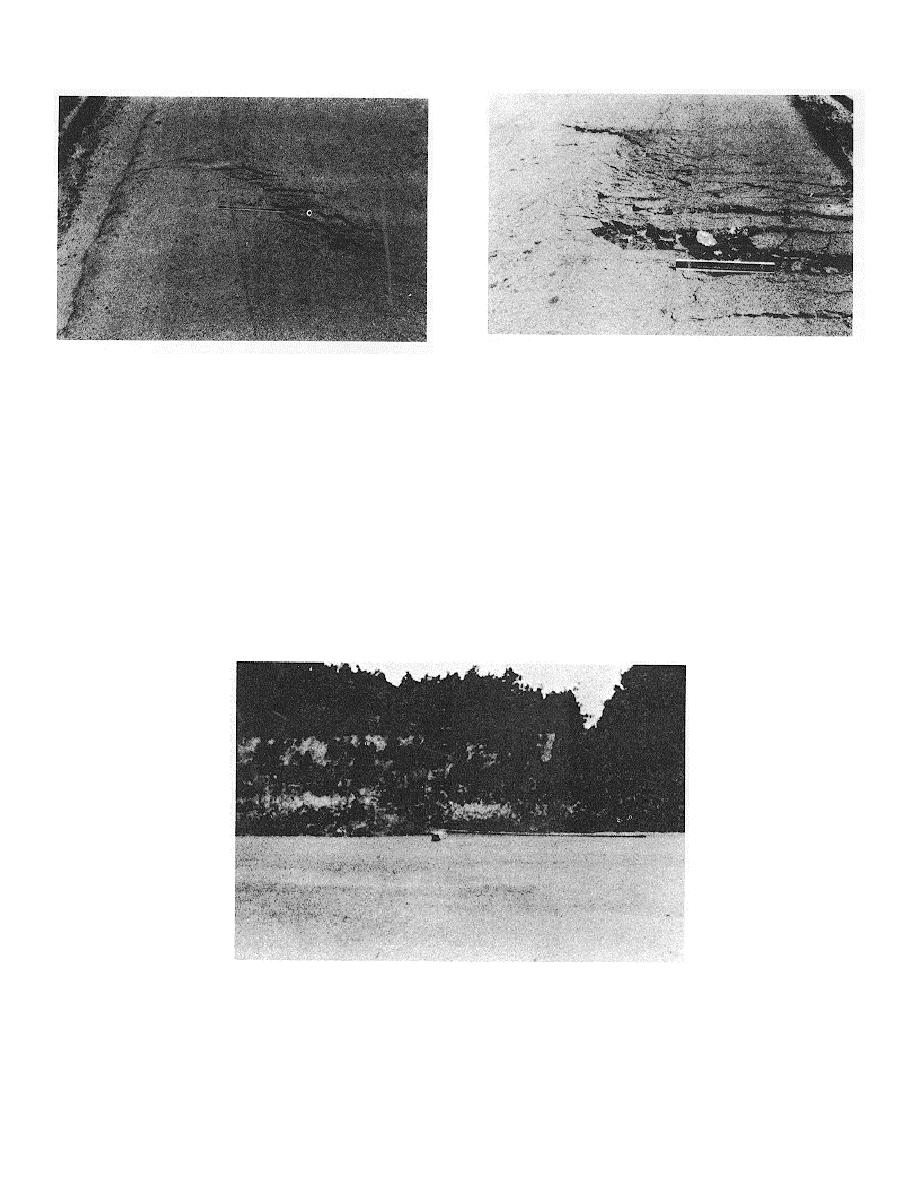
Figure B-65. High-severity slippage cracking.
Figure B-64. Medium-severity slippage cracking.
1. The average crack width is greater than 1I inches.
2. The area around the crack is broken into easily removed pieces.
How to Measure:
The area associated with a given slippage crack is measured in square feet and
rated according to the highest level severity in the area.
Name of Distress:
Swell.
Description:
Swell is characterized by an upward bulge in the pavement's surface-a long,
gradual wave of more than 10 feet long. Swelling can be accompanied by
surface cracking. This distress is usually caused by frost action in the
subgrade or by swelling soil.
Severity Levels:
L-Swell causes low-severity ride quality. Low-severity swells are not always easy
to see, but can be detected by driving at the speed limit over the pavement
section. An upward acceleration will occur at the swell if it is present. (See
fig B-66.) M-Swell causes medium-severity ride quality. (See fig B-66.) H-
Swell causes high-severity ride quality. (See fig B-66.)
Figure B-66. Example swell; severity level is based on ride quality criteria.
How to Measure:
The surface of the swell is measured in square feet.
Name of Distress:
Weathering and Raveling.
B-22



 Previous Page
Previous Page
