TM 5-623
DESIGN THICKNESS IN INCHES
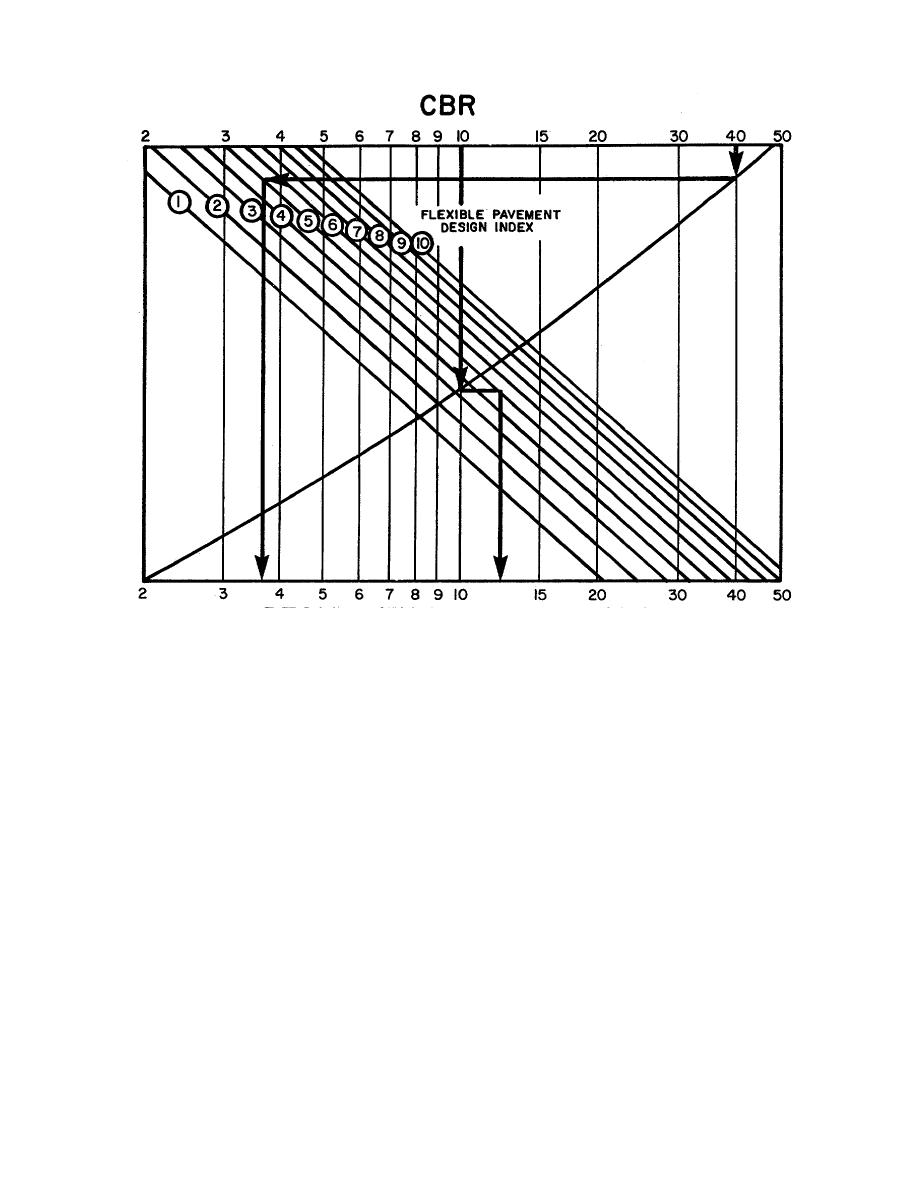
Figure 4-8. Thickness design requirements for flexible pavements (TM 5-822-5, 1 Oct 80, and AFM 88-24, Chap 3).
caused by excessive patching, limitations of manpower
g. Skid resistance/hydroplaning potential.
Skid
and equipment, and pavement mission requirements.
resistance and hydroplaning potential are only of
Therefore, the amount and types of maintenance
concern for high-speed-traveled roads and airfields.
previously applied to a pavement section must be
Pavement sections where skid is not of concern should
determined before a new strategy is selected. For
be listed as such on the pavement evaluation sheet.
example, a pavement with a large patched or replaced
Otherwise, skid resistance must be directly measured
portion may have had many distress problems which are
with special equipment. If direct measurement is not
likely to continue in the future, and which should be
possible, skid resistance/hydroplaning potential may be
considered in the new strategy.
evaluated by reviewing distress date. Distresses that
(2) The evaluation of previous maintenance
can cause skid resistance/hydroplaning potential are
can be based on the incidence of permanent patching
bleeding, polished aggregates, rutting, and depression
(asphalt pavements), large areas of patching (more than
(for asphalt pavements) and polished aggregate (for
5 square feet), and/or slab replacement (concrete
concrete pavements). In our example, figure 4-1, skid
pavement). Patching and/or slab replacement ranging
resistance of "Minor" was circled at line 7.
between 1.5 and 3.5 percent (based on surface area for
asphalt and number of slabs for concrete) is considered
h. Previous maintenance.
normal; more than 3.5 percent is considered high, and
(1) A pavement section can be kept in
less than 1.5 percent is considered low.
Some
operating condition almost indefinitely if extensive
pavement sections may have received an excessive
maintenance is performed. However, there are many
drawbacks to this maintenance strategy, including
overall cost, section downtime, increase in roughness
4-11



 Previous Page
Previous Page
