TM 5-822-13/AFJMAN 32-1018
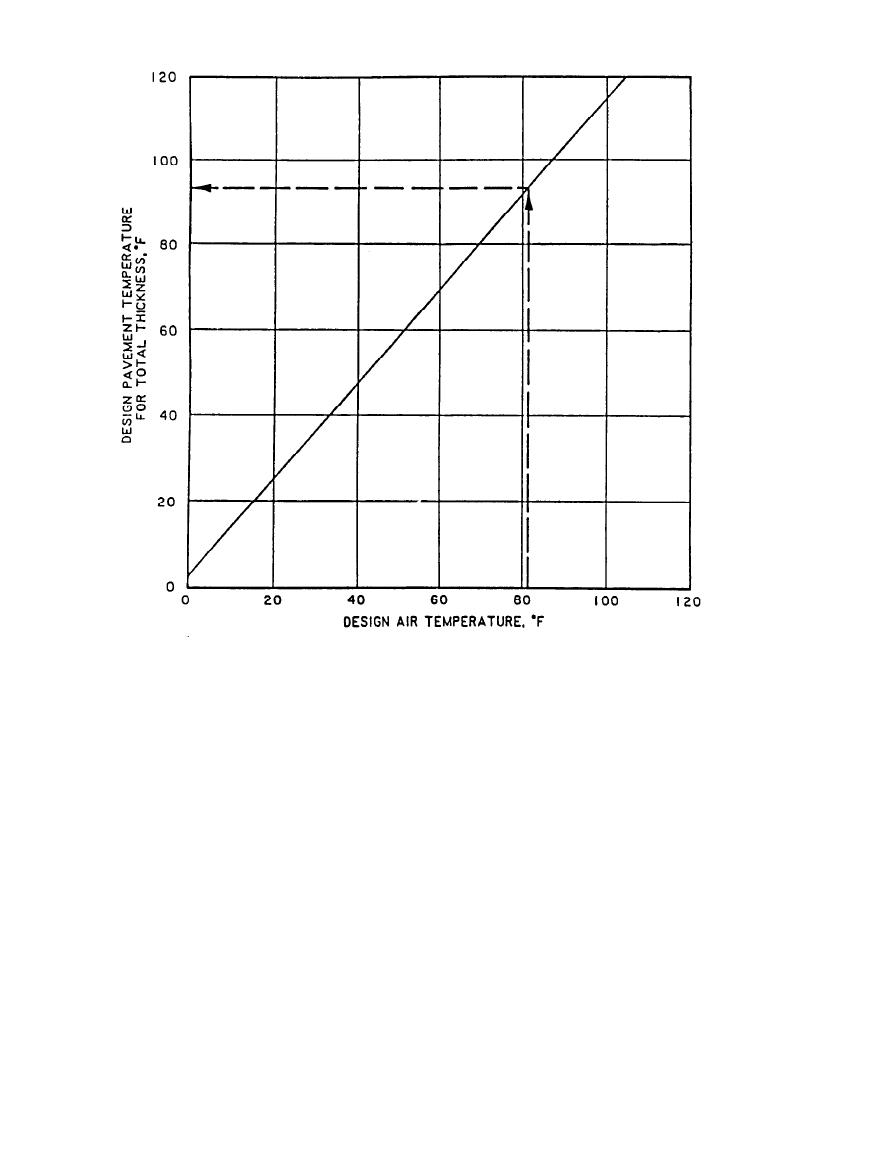
Figure 4-1. Relationship Between Design (Mean) Pavement Temperature and Design Air Temperature.
b. Thaw periods. The effects of temperature on subgrade materials are considered only with regard to frost
penetration. The basic requirements for frost protection are given in TM 5-822-5/AFM 88-7, Chap. 3.
c. Subgrade moisture content for material characterization. Pavement design is usually predicated on a
subgrade which is assumed to be near-saturation. The design may be based on subgrade with lower moisture
content if available field measurements indicate that the subgrade will not reach saturation. These measure-
ments must reflect the period of the year when the water table is at its highest level, and such designs must be
approached with caution.
4-2. Material characterization.
Characterization of the pavement materials requires the quantification of the material stiffness as defined by the
resilient modulus of elasticity and Poisson's ratio and, for selected pavement components, a fatigue strength as
defined by a failure criterion. The use of layered elastic design procedures does not negate the material require-
ments set forth in TM 5-822-5/AFM 88-7, Chap. 3.
a. Modulus of elasticity.
(1) Bituminous mixtures. The term "bituminous mixtures" refers to a compacted mixture of bitumen and
aggregate designed in accordance with standard practice. The modulus for these materials is determined by use
of the repetitive triaxial tests. The procedure for preparation of the sample is given in TM-5-825-2-1/AFM 88-6,
Chap. 2, Section A with the procedure for the conduct of the repetitive triaxial test given in chapter 9 of the
same manual.
(a) The stiffness of the bituminous mixtures will be greatly affected by both the rate of loading and
temperature. For roads and streets design, a loading rate of 2 to 4 hertz is recommended. Specimens should be
tested at temperatures of 40, 70 and 100 degrees F. so that a modulus-temperature relationship can be estab-
lished. If temperature data indicate greater extremes than 40 and 100 degrees F., tests should be conducted at
4-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
