UFC 3-240-13FN
25 May 2005
2-2.5.5
exchange and when the effluent waters from strong acid cation ion exchange and the
sodium ion exchange are mixed. Carbon dioxide dissolved in water can cause corrosion
in water lines, pump impellers, and vessels. As described in Chapter 3, the carbon
dioxide concentration must be kept as low as possible in the boiler feed water and in the
water entering steam condensate lines.
2-2.5.5.1
Methods of Decarbonation. Free carbon dioxide is commonly removed
in a degasifier or aerator (see paragraph 2-2.2). In steam systems and in high-
temperature water systems, removal of CO2 is usually achieved in the deaerator rather
than with a separate degasifier unit, although steam systems can have degasifiers.
2-2.5.5.2
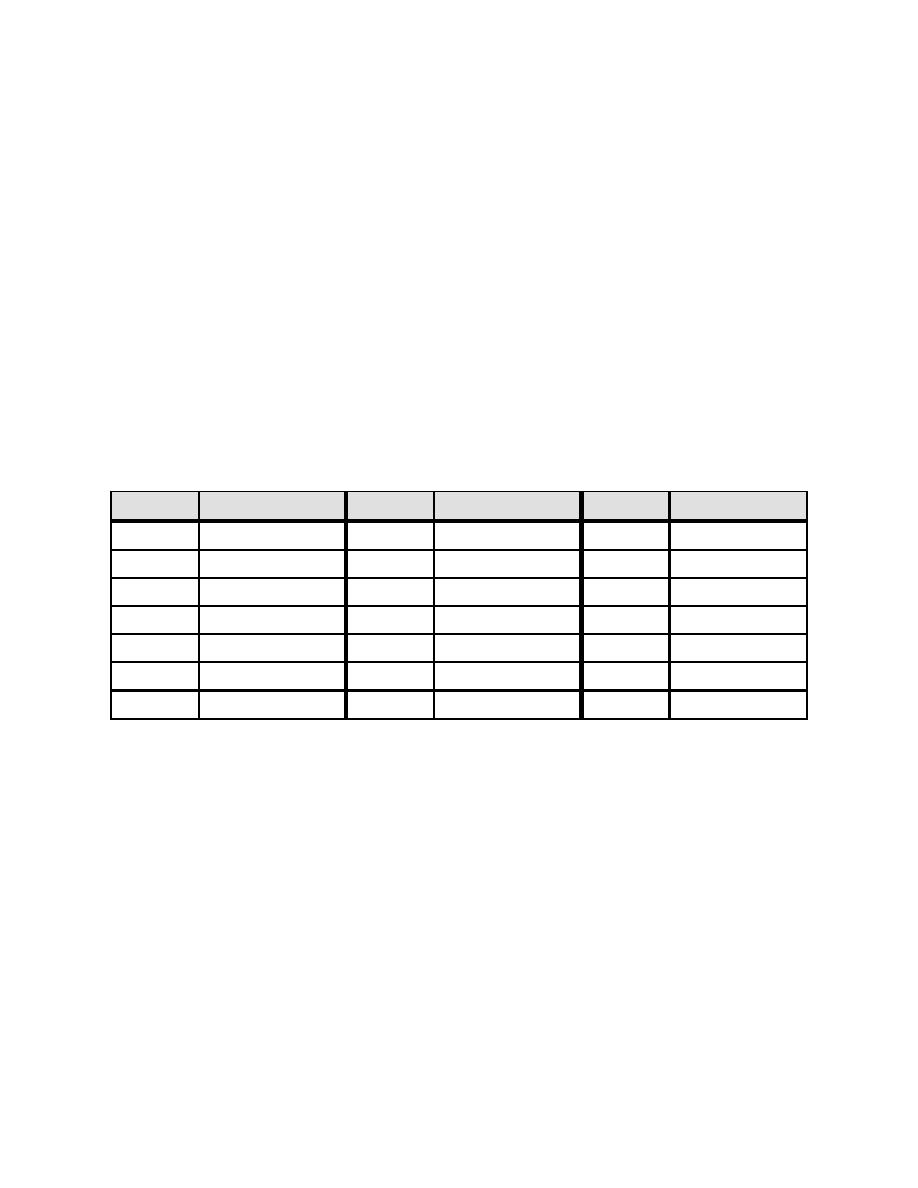
Analysis of Carbon Dioxide Content. By analyzing the water for the
hydrogen ion concentration (pH) and the total (M) alkalinity, the free carbon dioxide
content can be calculated (see Table 2-4).
Table 2-4. Carbon Dioxide Content of Water vs. pH
pH
CO2
pH
CO2
pH
CO2
5.4
4.4 M
6.6
0.45 M
7.3
0.099 M
6.0
1.9 M
6.7
0.38 M
7.4
0.079 M
6.1
1.5 M
6.8
0.31 M
7.5
0.062 M
6.2
1.23 M
6.9
0.24 M
7.6
0.050 M
6.3
0.92 M
7.0
0.19 M
7.7
0.040 M
6.4
0.75 M
7.1
0.15 M
7.8
0.033 M
6.5
0.62 M
7.2
0.12 M
7.9
0.026 M
NOTES:
1. At pH levels of 8.0 or higher, the free CO2 content is negligible.
2. "M" is total alkalinity (as calcium carbonate [CaCO3]).
EXAMPLE 2-2:
a) Total alkalinity (M) of an inlet water to a degasifier is 100 ppm and the pH
is 6.8.
CO2 content = Value x M = 0.31 x 100 = 31 ppm
b) The outlet pH is 7.9, so the CO2 content will be (let M = 80, since some
alkalinity was removed as CO2):
CO2 content = 0.026 x 80 = 2.1 ppm
28



 Previous Page
Previous Page
