TM 5-814-3/AFM 88-11, Volume III
6-6. lmhoff tanks.
Perhaps the main weak point of a septic tank involves the attempt to combine sedimentation and decomposi-
tion of accumulated sludge in the same tank. Rather than use a heated digester, another system was devised
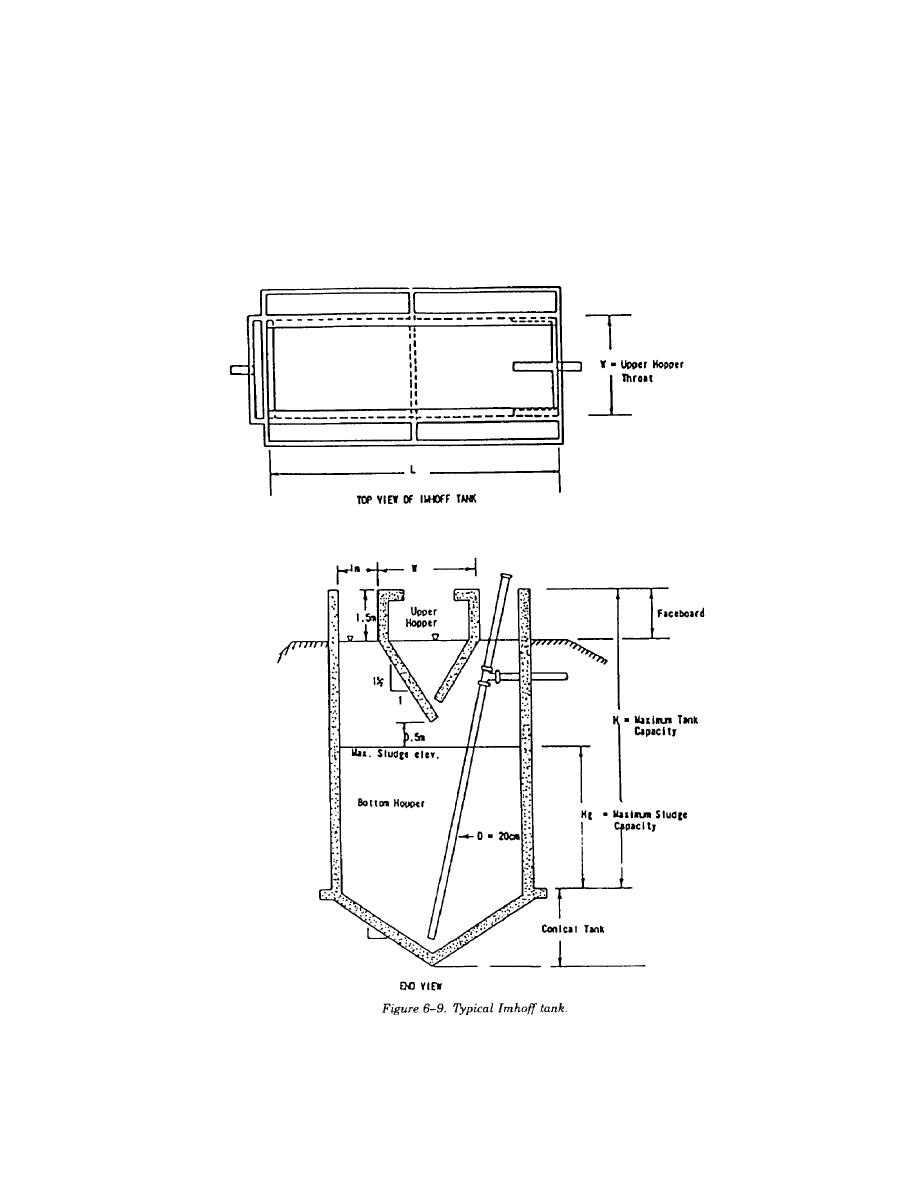
now known as the "Imhoff tank," In these tanks, sedimentation is separated from digestion. Solids that settle
in the upper portion of the tank pass through a slot into a bottom hopper. Here, the sludge digests and, once
stabilized, may be periodically removed from the bottom of the vee-shaped or conical tank for subsequent
further treatment. Gases produced by the decomposition of the sludge are vented along the sides of the lower
compartment and are not allowed up to the sedimentation chamber. De-sludging is carried out about 4 times
each year at a moisture content of 93 percent. A typical design is shown in figure 6-9.
a. Operational considerations. Operating problems include the following: foaming, scum formation, and
offensive odors. A high "freeboard" unit will insure that foam and scum are retained. Their accumulation will
allow the development of a homogeneous layer from which a light sludge may be periodically removed when
6-16



 Previous Page
Previous Page
