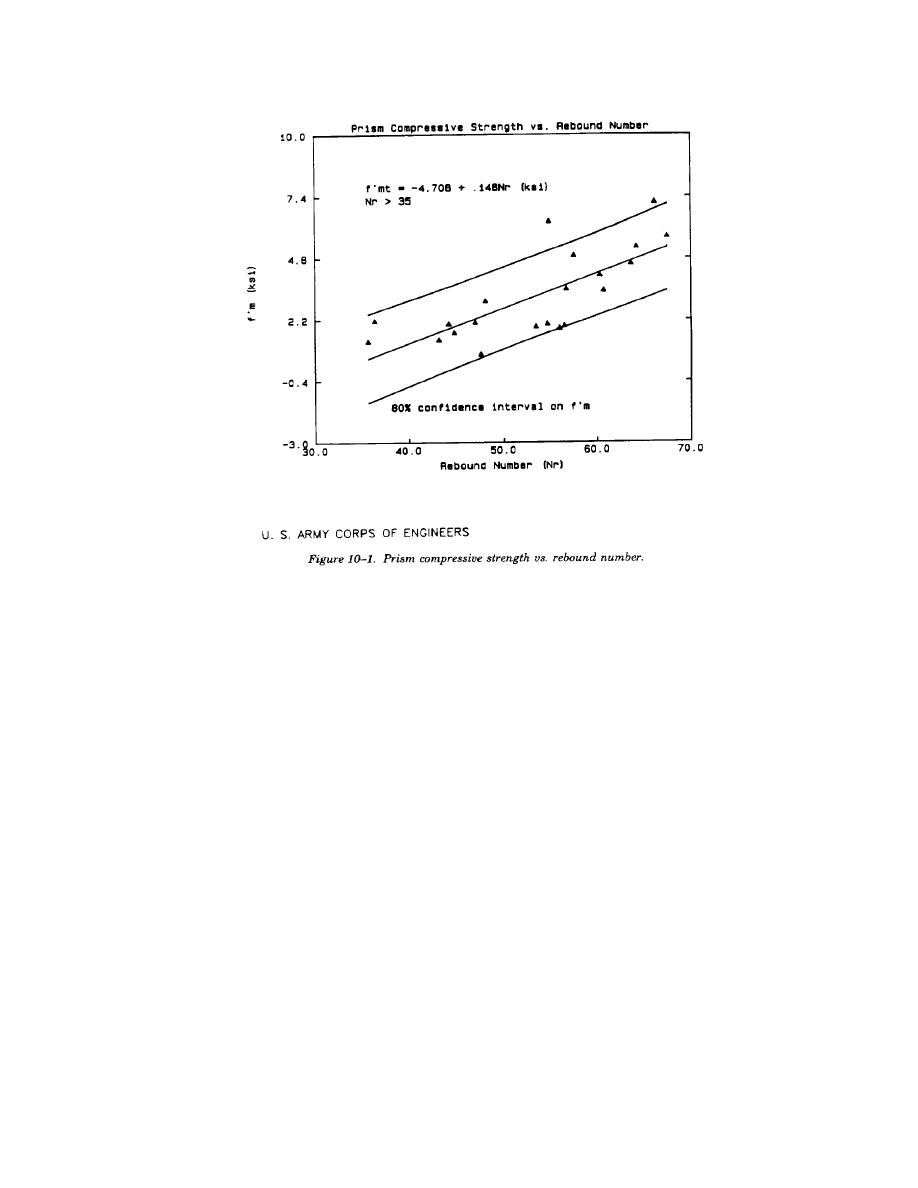
TM 5-809-3/NAVFAC DM-2.9/AFM 88-3, Chap. 3
(1) In-situ stress test. Evaluation of the in-
(2) In-situ deformability test. The
situ compressive stress is a simple process of stress
deformation properties of masonry may be
relief induced by the removal of a portion of a
evaluated by inserting two parallel flatjacks, one
mortar bed joint followed by restoration of the
directly above the other separated by several
original state of stress by pressurizing a flatjack
courses of masonry, and pressurizing them equally,
inserted in the slot created by the removal of the
thus imposing a compressive load on the
mortar. When the mortar is removed from a
intervening masonry. The deformations of the
horizontal joint, the release of the stress across the
masonry between the flatjacks are then measured
joint causes the slot to close by a small amount.
for several increments of load. The results are used
The magnitude of this deformation is measured
to calculate the masonry deformability modulus. If
using a removable dial gauge between two or more
some damage to the masonry is acceptable, the
points located symmetrically on either side of the
masonry may be loaded to failure to determine the
slot. A flatjack is then inserted in the slot and
maximum strength. This technique is useful when
pressurized until the original position of the meas-
an estimate of material deformability or strength is
uring points is restored. At this point the pressure
needed for stress analysis or deflection calculations.
in the flatjack, modified by two constants to
Test results in the form of a cyclic stress-strain
account for the flatjack stiffness and the area of the
curve along with the test setup are shown in figure
slot, is assumed equivalent to the original vertical
10-3. This in-situ deformability test provides a
compressive stress in the masonry. The technique
reasonably accurate measure of masonry compres-
is useful for verifying analytical models or for
sive modulus, typically overestimating the masonry
determining stress distributions in masonry walls
stiffness by approximately 10%.
(3) Equipment. A flatjack is a thin steel
when conditions of loading or displacement are
unknown or difficult to quantify. Typical test
bladder that is pressurized with oil to apply a
results, as shown in figure 10-2, are a plot of
uniform stress over the plan area of the flatjack. In
masonry deformations around a slot for various
masonry structures, flatjacks are inserted in slots
levels of internal flatjack pressure. Past results
cut in mortar bed joints. Flatjacks may be made in
show that the in-situ stress test is able to estimate
many shapes and sizes. Flatjacks with curved edges
the actual state of masonry compressive stress to
are designed to fit in a slot cut by a circular
within 10% to 15%.
masonry saw and rectangular jacks are used where
10-3



 Previous Page
Previous Page
