TM 5-809-3/NAVFAC DM-2.9/AFM 88-3, Chap. 3
embedded. Test hammers are available in four basic
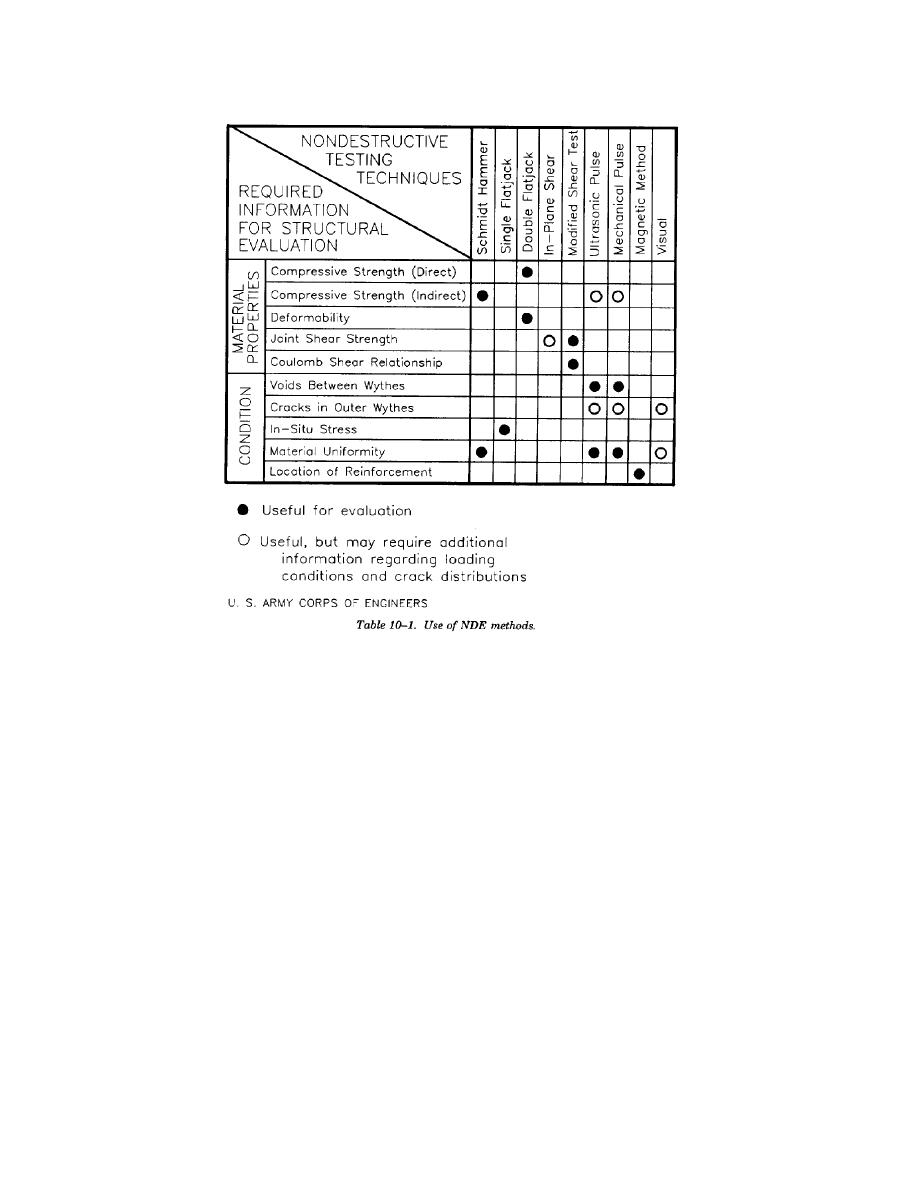
but only for evaluation of material uniformity. The
varieties; Type L, .Type N, Type M, and Type P;
correlation to masonry compressive strength is
which are distinguished primarily by their impact
useful primarily for determining the expected
energy. The type N hammer has a tendency to
relative change in compressive strength between
crush the brick unit material under the tip,
locations with different rebound numbers.
b. Flatjack methods. The flatjack test is being
particularly for older, lightly burned units. For this
reason, a type L hammer with lower impact energy
recognized as a powerful tool for NDE of the
is recommended to prevent damage to the masonry
structural properties of masonry. ASTM standards
units.
are currently being established for the application
(2) Use. The application of the Schmidt
of flatjack testing to the evaluation of unreinforced
Hammer to concrete testing is governed by ASTM
solid clay unit (brick) masonry. The test has been
C 805. There is no standard at this time for the use
successfully applied to cut stone masonry. Under
of the Schmidt Hammer on masonry materials. An
the proper conditions, flatjacks can provide infor-
experimental procedure has been adopted for test-
mation on the in-situ state of stress at virtually any
ing masonry structures which is based upon the
point in a masonry structure. The test provides a
International Society for Rock Mechanics (ISRM)
measure of the deformability of the masonry
suggested method for determining Schmidt re-
materials and in some cases, a direct measure of
bound hardness. While laboratory tests have shown
masonry compressive strength. No other NDE test
that a relationships may exist between rebound
method offers direct physical measurement of
number and masonry compressive strength under
material and structural properties without any
controlled conditions, the general applicability of
reliance on empirical correlations. The two main
such a relationship has not been verified. Therefore,
types of flatjack tests; the in-situ stress or single-
due to the wide variations in predicted strength, it
flat jack test and the in-situ deformability or two-
is not recommended that the Schmidt Hammer be
flatjack test; are described in the following
used for direct prediction of compressive strength,
paragraphs:
10-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
