UFC 3-280-03
23 JULY 2003
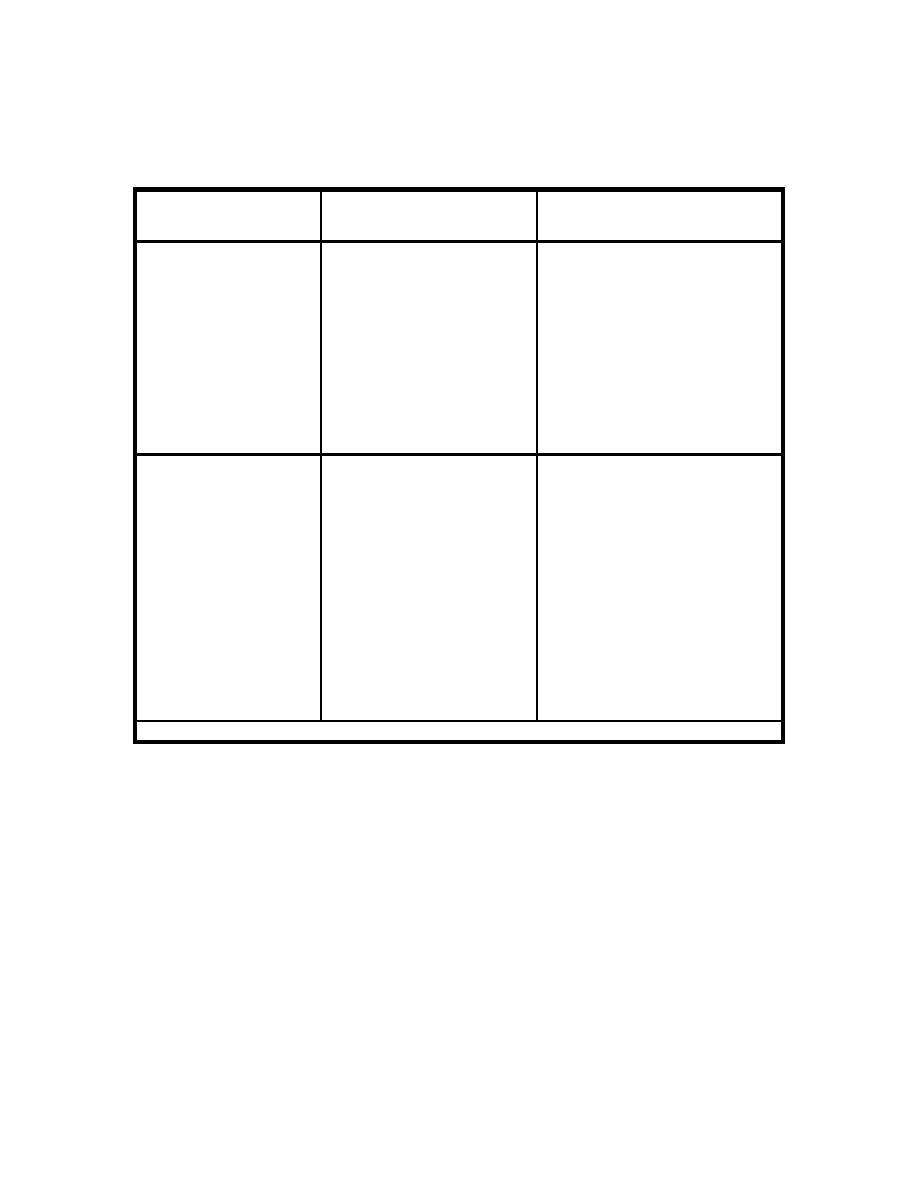
Table 2-3. Advantages and disadvantages of fixed-volume versus
variable-volume filter presses.
Type of Dewatering
Advantages
Disadvantages
Process/Device
Dewaters only well conditioned
Fixed-Volume Press
Higher volumetric capacity
sludges.
requires fewer dewatering
cycles per day.
More chemicals required for
conditioning.
Less complex instrumentation.
Longer cycle time/per unit volume of
Fewer moving parts.
sludge.
Longer plate life.
Lower maintenance.
Limited volumetric capacity, requires
Variable-Volume Press
Dewaters marginally
more cycles per day.
conditioned sludges.
Mechanically complex.
Shorter cycle time.
Complex instrumentation.
Fewer chemicals required for
conditioning.
Labor intensive filter cloth
replacement.
Lower operation and
maintenance for sludge feed
Higher maintenance.
pumps.
Precoating system is not
required.
Source: EPA (1982a, 1986)
2-3.2.1 Advantages. As shown in Table 2-2, plate and frame filter presses have
several advantages compared with other sludge dewatering systems. A high cake solids
content (typically 30 to 50%) can be achieved, which is 6 to 10% higher than that
achieved with other dewatering systems. A very high solids capture (98%) can be
obtained. High filtrate quality can be achieved, which lowers recycle stream treatment
requirements. This system can dewater hard-to-dewater sludge and sludge of varying
characteristics and is mechanically reliable. In addition, this type of system may be the
only one capable of dewatering sludge dry enough to meet landfill requirements in some
areas.
As shown in Table 2-3, the variable-volume press system has several advan-
tages over the fixed-volume press system. First, the variable-volume system produces a
dryer cake (typically 3 to 5%) of more uniform moisture content. Second, the variable-
volume press has a shorter cycle time and, thus, a higher production throughput. This
shorter cycle time is a result of the more effective and uniform pressure placed on the
sludge during the dewatering process. Other advantages of the variable-volume filter
2-14



 Previous Page
Previous Page
