TM 5-822-2/AFM 88-7, Chap. 5
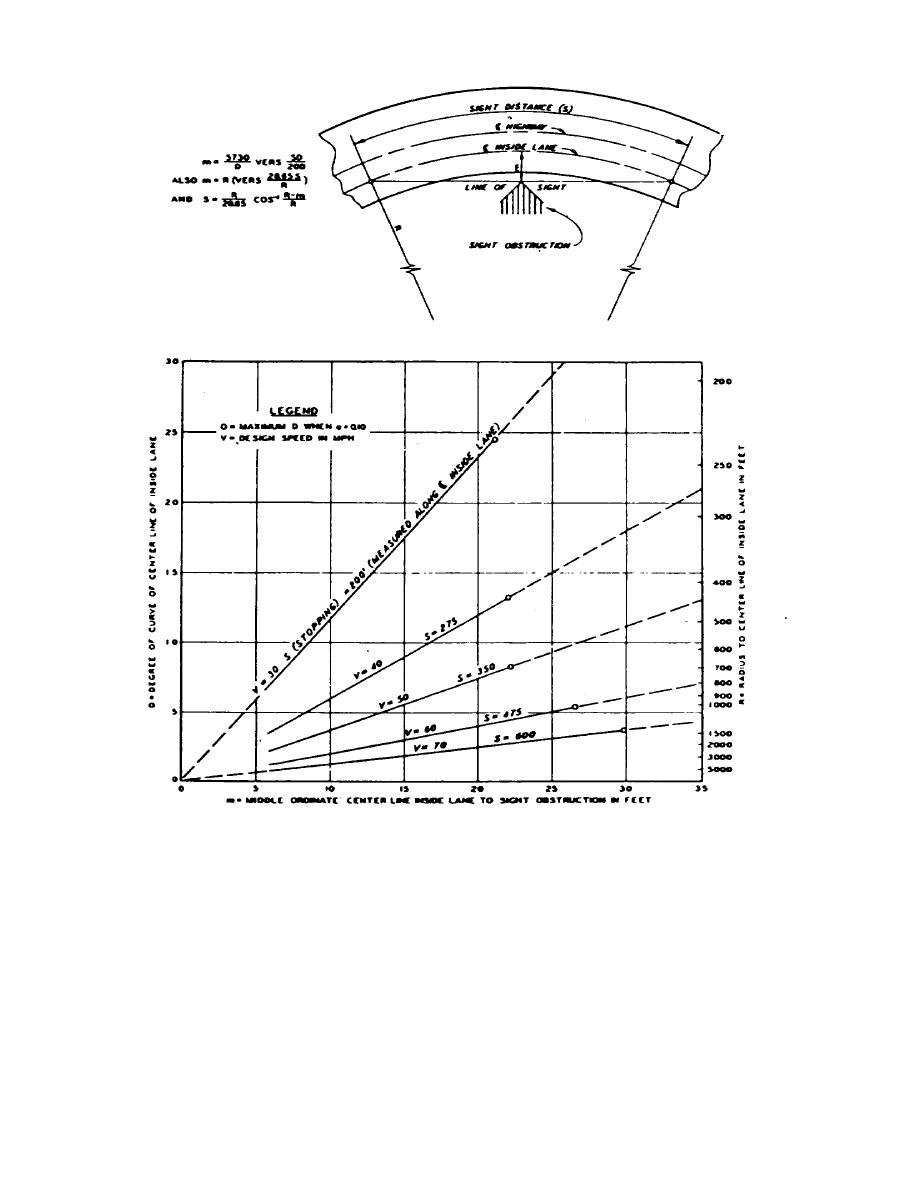
Figure 3-4. Stopping sight distance on horizontal curves and open road conditions.
or economically feasible.
Minimum sight distance
K = horizontal distance in feet required to
required for safety must be provided in all cases.
effect a 1 percent change in gradient
Vertical curves may be any one of the types of simple
A = algebraic difference of tangent grades,
parabolic curves shown in figure 3-5. There are three
percent
length categories for vertical curves: maximum, length
required for safety, and minimum. All vertical curves
Values for K for use in determining the length of vertical
should be as long as economically feasible. The length
curves required for safety are shown in tables 1-1 and 1-
of a vertical crest or sag curve required to provide
2. The minimum length of vertical curves is also shown
minimum stopping distance is determined by the
in tables 1-1 and 1-2. In each case the minimum length
following formula:
is equal to three times the design speed.
e. Cross section. Figures 3-6 and 3-7 illustrate
L = KA
(eq 32)
where
typical combinations of cross-section elements for which
L = length of curve, feet
geometric design criteria are outlined in tables 1-1 and 1-
2.
3-17



 Previous Page
Previous Page
