UFC 3-240-13FN
25 May 2005
optimal for the use of bromine. Bromine release agents include dry chemicals called
hydantoins and bromine salts, such as sodium bromide. When a salt solution is mixed
with an oxidizing agent, such as bleach, and a reaction occurs, bromine is produced. In
water, bromine degrades more rapidly than chlorine. Recent developments in bromine
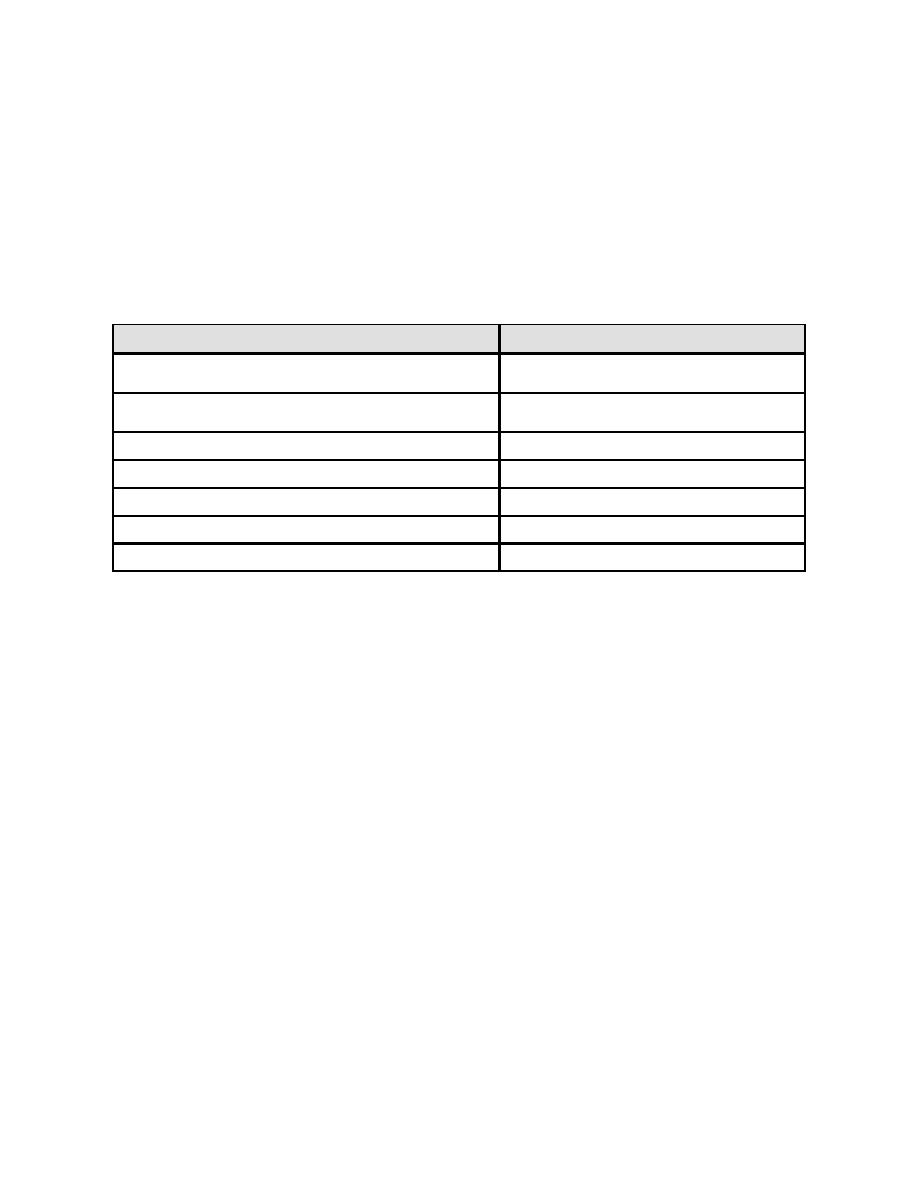
chemistry have resulted in the production of a bromine solution (liquid). Table 4-5 shows
examples of some bromine release agents. The most popular sources of bromine are
the dry bromine release products.
Table 4-5. Bromine Release Agents
Release Agent
Comments
Dry product releases bromine
Bromo-chloro-dimethyl hydantoin
Dry product releases bromine
Bromo-chloro-methyl-ethyl hydantoin
Isocyanuric acid plus sodium bromide
Dry product releases bromine
Chlorine plus sodium bromide
Produces bromine liquid
Peroxide plus sodium bromide
Produces bromine liquid
Ozone plus sodium bromide
Produces bromine liquid
Stabilized bromine
Hydrobromite liquid
4-4.4.1.3
Ozone. Ozone (O3) is a gas produced by passing dry air either through a
strong electric field or near an ultraviolet light. If ozone is dissolved in water, the
resulting solution can be added to cooling water. Ozone is a very strong oxidizing
biocide that, if properly applied, can provide effective control of microorganisms in
cooling tower systems; however, because of safety and operational problems
associated with its manufacture and use, and the resulting high capital and operating
costs, it is neither the most economical method nor the preferred method for
microbiological control in cooling towers under normal operations. Ozone can increase
metal corrosion and does not prevent scale (see paragraph 8-2.9.1).
4-4.4.1.4
Chlorine Dioxide. Chlorine dioxide (ClO2) is a gas generated by mixing
several chemicals. The chlorine dioxide gas produced in this manner is subsequently
dissolved in water, with the water containing the chlorine dioxide then added to the
cooling water. Chlorine dioxide must be produced in close proximity to the point of use.
It is not recommended for use on military installations due to the complexity of its
production and safety concerns associated with its production and handling.
4-4.4.1.5
used at a concentration of 30% in water. Hydrogen peroxide is considered one of the
most environmentally friendly oxidizing biocides because it degrades to water; however,
concentrated hydrogen peroxide will react in a violent manner when it comes into
contact with organic chemicals and materials.
119



 Previous Page
Previous Page
