UFC 3-240-13FN
25 May 2005
they coat the metal; however, you should not use them in condensate systems that
have had corrosion problems in the past. Excess adsorption of the filming amine on the
rust will occur and the amine can dislodge the rust and cause it to be returned to the
deaerator or to the boiler. Adding filming amines continuously during operation and
directly into the steam header through a quill, instead of into the steam drum, is
essential. Addition of inadequate dosages can result in accelerated pitting-type
corrosion due to incomplete surface coverage. You may need written authorization from
the appropriate source before using filming amines in military boilers.
3-2.7.5
Control of Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen by Specialty Volatile Amines.
Some of the specialty oxygen scavengers described in paragraph 3-2.6.2.2 for boilers
over 6205 kilopascals (900 pounds per square inch gauge) can be used for the purpose
of control of both carbon dioxide and oxygen. The specialty volatile amines include
hydroxylamine, hydroquinone, carbohydrazide, hydrazine sulfate, and erythorbic acid.
They work by both raising the pH of condensate and by scavenging oxygen. They also
passivate metal surfaces. Their use may not be appropriate and is restricted by the
Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Note that these chemicals may not be needed for
good operation of military boiler plants.
3-2.7.6
Amine Limitations and Indoor Air and Steam Quality Issues. 21 CFR
Part 173.310 restricts using common neutralizing amines and filming amines to the
limitations summarized in Table 3-6. Note that the limits shown in Table 3-6 are
maximum allowable concentrations. Using amines may not always be advisable. If
amine addition is not continuous, or if the boiler operation is cyclic (e.g., shutting down
the boiler for several hours each day), the maximum amine concentration may vary
widely and exceed limits, even though the average concentration is within the limits.
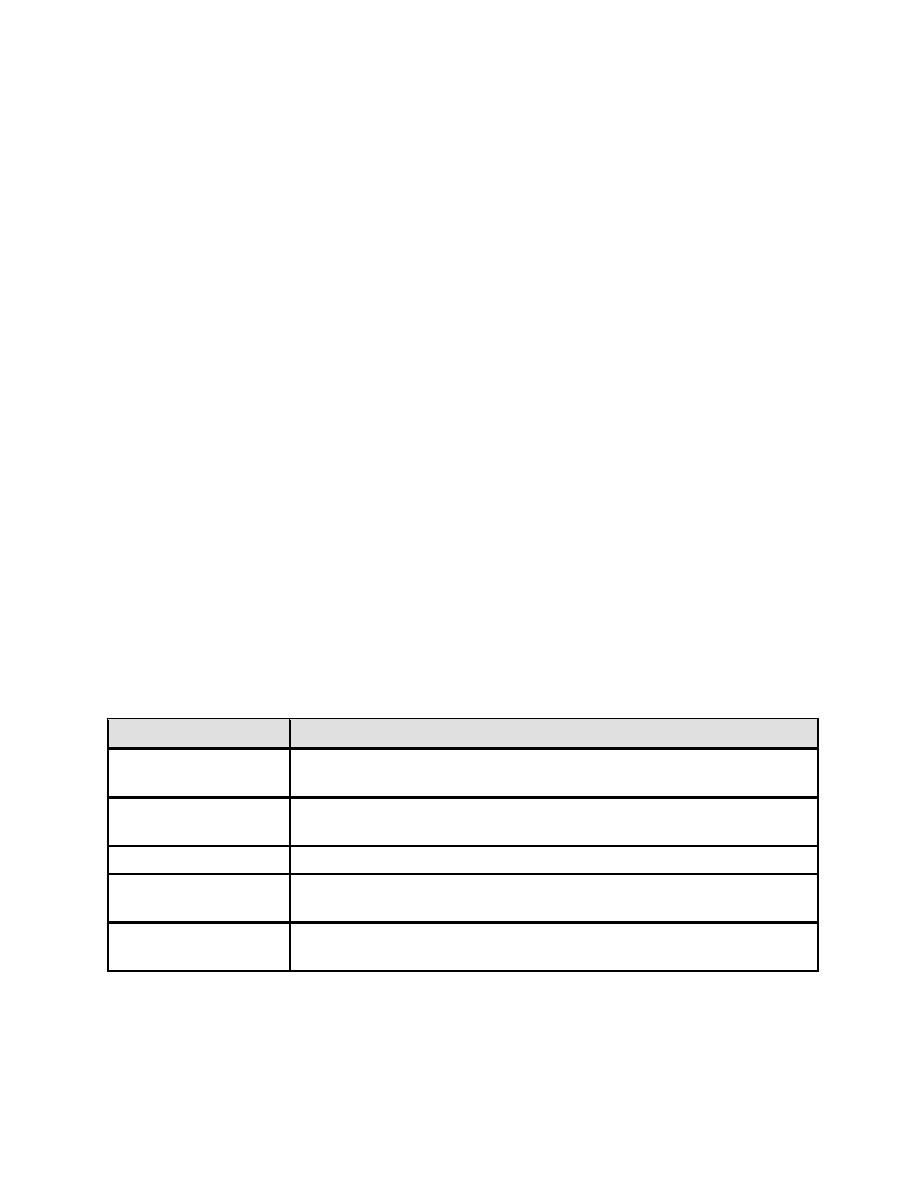
Table 3-6. Amine Limits
Amine
Limitation
Not to exceed 10 ppm in steam, and excluding steam in contact
Cyclohexylamine
with milk and milk products.
Not to exceed 15 ppm in steam, and excluding steam in contact
DEAE
with milk and milk products
Hydrazine
Zero in steam.
Not to exceed 10 ppm in steam, and excluding steam in contact
Morpholine
with milk and milk products.
Not to exceed 3 ppm in steam, and excluding steam in contact
Octadecylamine
with milk and milk products.
3-2.7.6.1
Steam Used for Sterilization. Some facilities, hospitals in particular, use
steam in autoclaves for the purpose of sterilizing equipment such as surgical
instruments. There is often concern that neutralizing amines may leave an amine
64



 Previous Page
Previous Page
