TM 5-814-3/AFM 88-11, Volume III
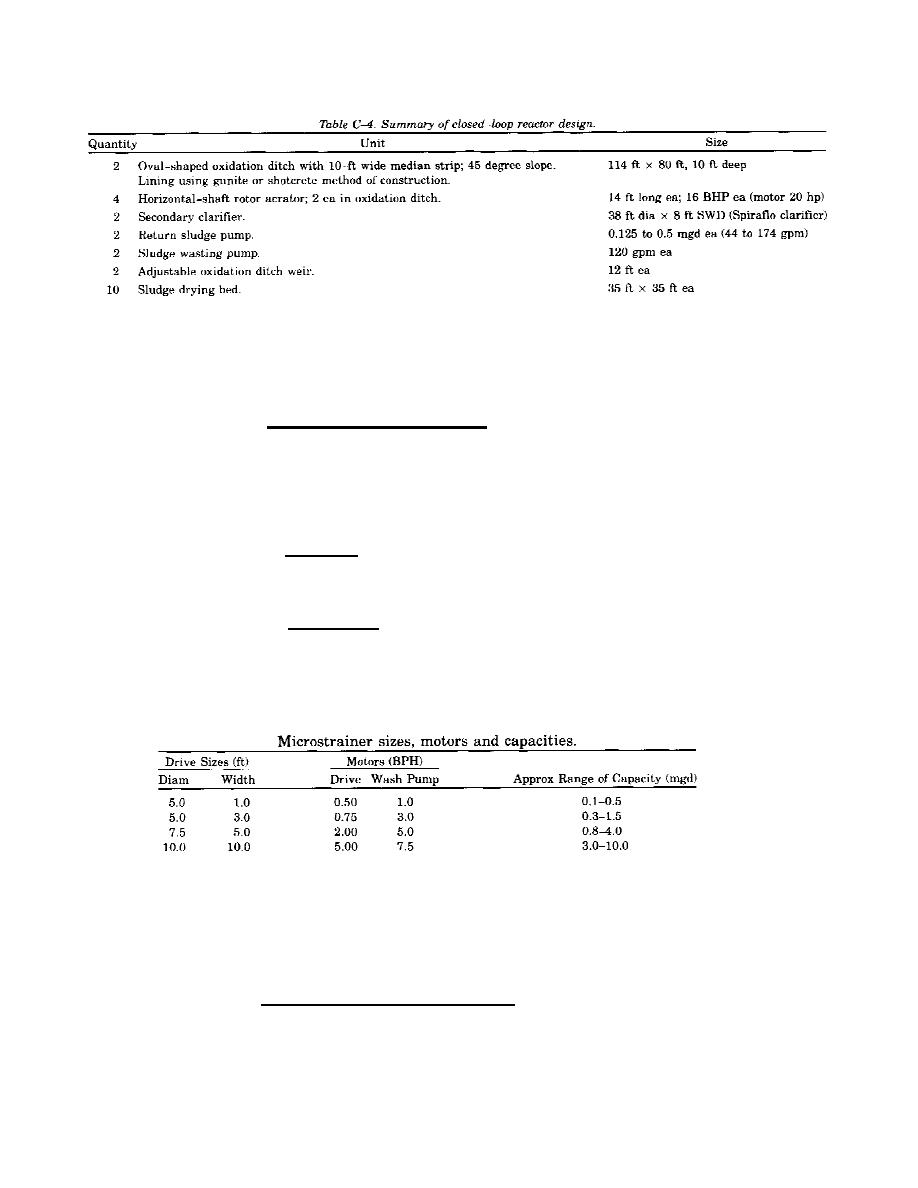
Table C-4 summarizes the design criteria for the horizontal-shaft aerators and multiple-ditch units.
C-9. Microstrainer. (Refer to para 15--4.)
a. Design requirements. Determine the solids loaidng on a microstrainer, treating a secondary effluent
containing 15 mg/L suspended solids, at a flow rate of 0.8 mgd.
b. Calculations and results.
(1) Determine screen surface area, using a hydraulic loading of 600 gal/sq ft/hr.
800,000 gal/day day/24 hr
Surface area '
' 55.6 sq ft, use 60 sq ft;
600 gal/sq ft/hr
Assumingb of the drum surface area is submerged: a drum, 5 ft dia 3 ft wide, would provide 32 sq ft of
submerged screen area.
(2) The solids loading is determined as follows:
Solids loading in lb/mil gal = SS concentration in mg/L8.34;
lb/mil gal
' 125 lb/mil gal;
15 mg/L 8.34
mg/L
125 lb/mil gal 0.8 mgd = 100 lb/day;
c100 lb/day
Solids loading =
' 3.1 lb/sq ft/day.
32.0 sq ft
This loading is high and might require solids removal pretreatment if screen clogging occurs.
The required horsepower is taken from the following tabulation (Source: EPA Design Manual for
Suspended Solids Removal):
C-10. Multi-media filtration. (Refer to para 15--5.)
a. Design requirements. Determine the size of a multi-media gravity filter used in treating a secondary
effluent, assuming a hydraulic loading of 5 gpm/sq ft and a flow rate of 0.7 mgd.
b. Calculations and results.
(1) Surface area:
Surface area = 700,000 gal/day day/1,440 min ' 97.2 sq ft, use 100 sq ft;
5 gal/min/sq ft
Provide two 50 sq ft filter units.
C-32



 Previous Page
Previous Page
