TM 5-818-5/AFM 88-5, Chap 6/NAVFA
P-418
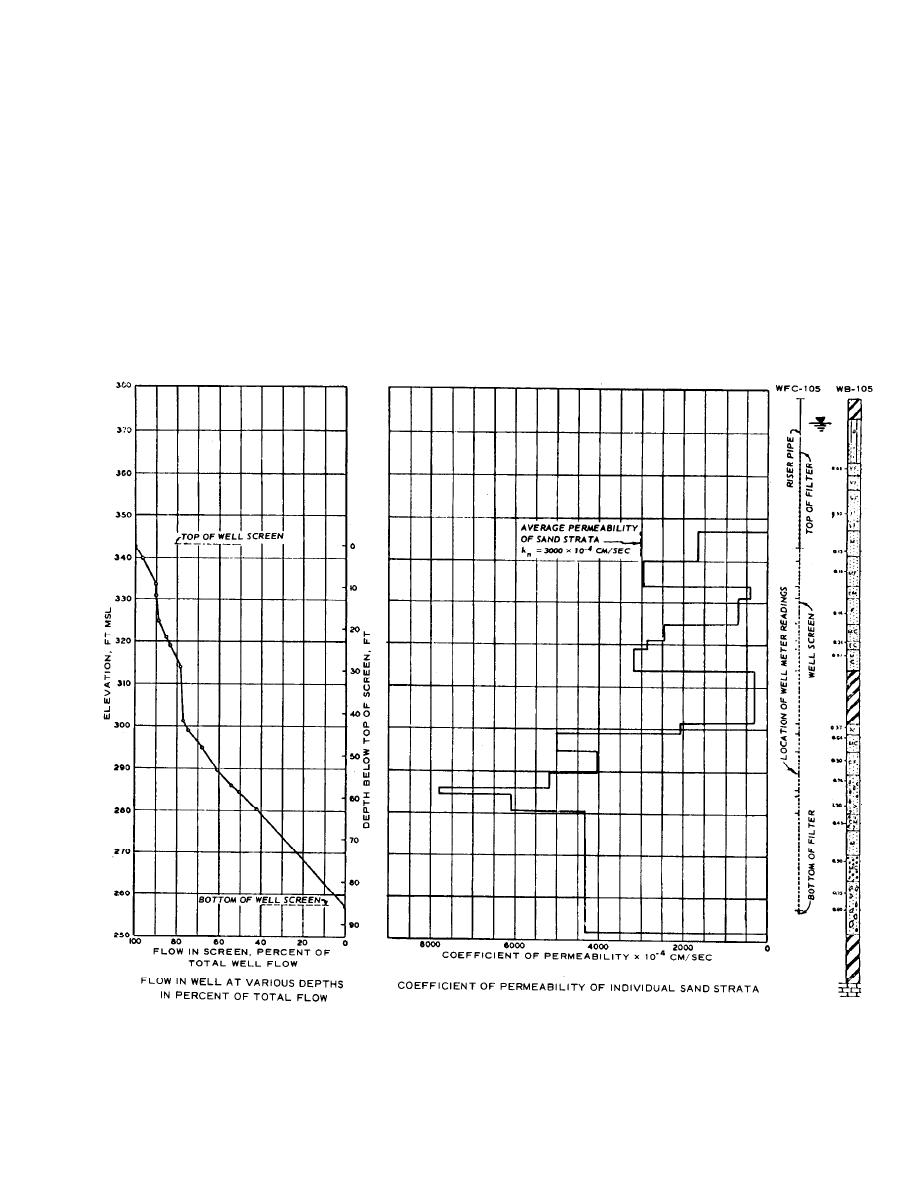
(1) The discharge from the well can be measured
termine the permeability of the various strata of the
by means of an orifice, pitometer, venturi, or flow-
formations in order to better determine the required
meter installed in the discharge pipe, or an orifice in-
length and depth or well screens of wellpoints for the
stalled at the end of the discharge pipe, as described in
design of a dewatering or drainage system. This
appendix G. The flow can also be estimated from the
permeability can be determined by measuring the
jet issuing from a smooth discharge pipe, or measured
vertical flow within the well screen at various levels
by means of a weir or flume installed in the discharge
with a flowmeter. The flow from the various strata can
channel. For such flow measurements, appropriate
be obtained by taking the difference in flow at adja-
consideration must be given to the pipe or channel hy-
cent measuring levels; the flow-meter, equipped with a
draulics in the vicinity of the flow-measuring device.
centering device, is placed in the well before the pump
Formulas, graphs, and tables for measuring flow from
is installed. Typical data obtained from such well-flow
a test well are given in appendix G.
measurements in a test well are shown in figure C-4.
(2) In thick aquifers, or in deposits where the
These data can be used to compute the coefficient of
material varies with depth, it may be desirable to de-
permeability of the various strata tested as shown. The
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
Figure C-4. Coefficient of permeability kh of various strata determined from a pumping test and flow measurements in the well screen.
C-4



 Previous Page
Previous Page
