TM 5-818-1 / AFM 88-3, Chap. 7
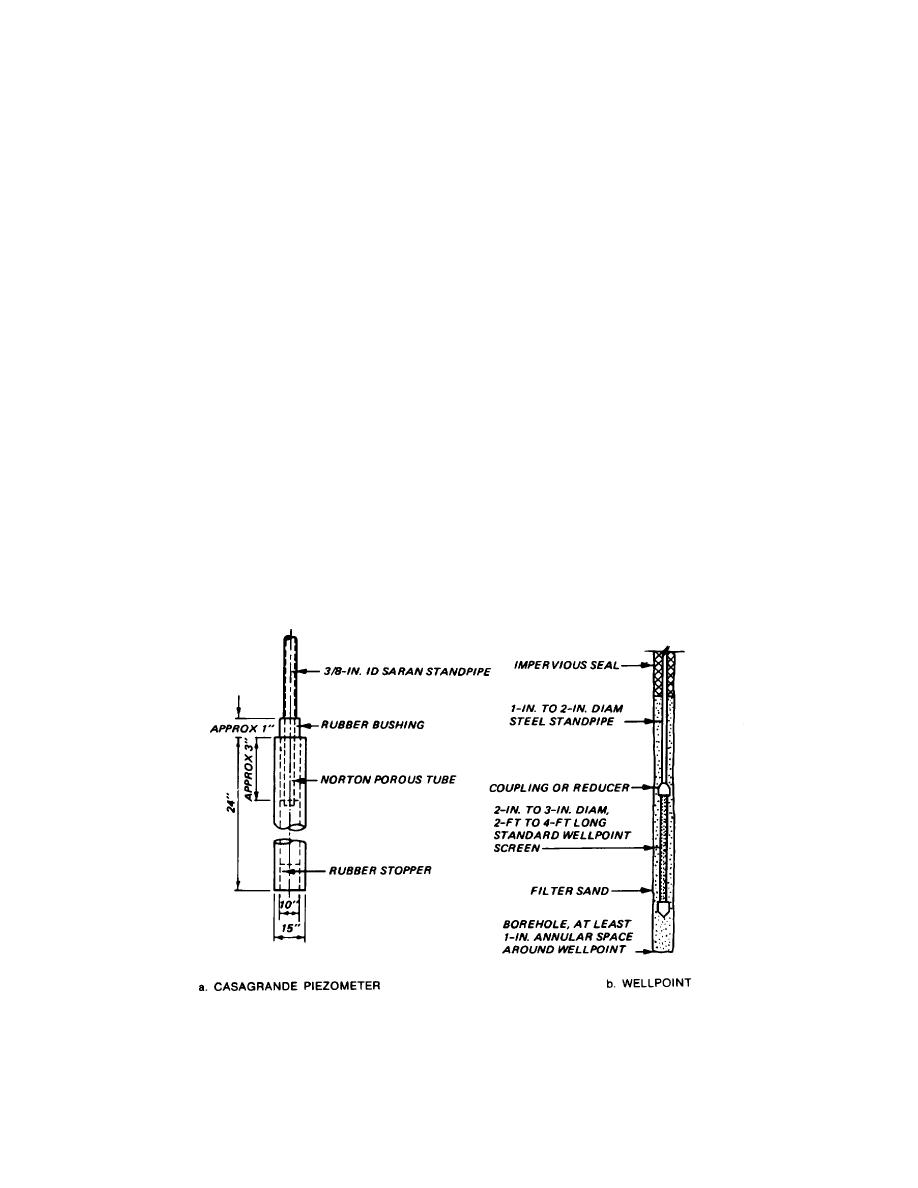
grande-type piezometer (fig 4-5) is recommended. The
performing field pumping tests are described in TM 5-
water level in the piezometer is determined by means of
818-5/AFM 88-5, Chapter 6.
a plumb line or sounding device. If the piezometric level
is above ground surface, a manometer or a Bourdon
4-6.
In situ load tests. Load tests are commonly
gage can be connected to the riser pipe to greatly
made on test piles to confirm design capacity and may
decrease the time for equilibrium to be achieved. If
occasionally be used to determine bearing capacity and
rapidly changing pore water pressures in clay are to be
settlement characteristics.
In general, specialized
determined, use closed system piezometers.
equipment and procedures are required to perform load
tests and considerable judgment and expertise must be
c. Field pumping tests.
Where accurate
employed to interpret results. Plate load tests are
knowledge of the permeability of the foundation soils is
occasionally used for bearing capacity determinations.
necessary, field pumping tests offer the most reliable
means. A rough estimate of the average permeability of
4-7.
Geophysical
exploration.
Geophysical
the material around the bottom of a cased drill hole may
methods of subsurface exploration are well suited for
be obtained by lowering or raising the water level in the
large sites due to the increasing cost of borings. Table
casing and observing the rise and fall of the water level
4-4 summarizes those geophysical methods most
as a function of time with respect to the stabilized
appropriate for site exploration. These methods are
piezometric water level (TM 5-818-5/AFM 88-5, Chapter
useful for interpolation between borings. Geophysical
6, para 38). A field pumping test is best per- formed by
data must be used in conjunction with borings and
pumping from a well in which a constant flow is
interpreted by qualified experienced personnel, or
maintained until the drawdown has stabilized, and when
misleading information is almost certain to result. The
groundwater levels are measured at several remote
two most applicable geophysical methods for exploring
borings or piezometers. It is desirable that well screens
foundations currently in use are seismic refraction and
fully penetrate the strata for which the permeability is to
electrical resistivity. Information secured by seismic
be measured. Formulas for computing the overall
refraction is primarily depth to bedrock and delineation of
permeability of a pervious stratum exhibiting gravity or
interfaces between zones of differing velocities. An
artesian flow are shown in figure 3-5. The formula for
electrical resistivity survey is superior in differ-
the special case of a fully penetrating well and artesian
aquifer is given as an example in figure 4-6. Methods for
U. S. Army Corps of Engineers
Figure 4-5. Typical details of Casagrande piezometer and piezometer using uwell screen.
4-9



 Previous Page
Previous Page
