TM 5-852-5/AFR 88-19, Volume 5
CHAPTER 3
WATER SOURCE DEVELOPMENT
3-1. General.
tion of the permafrost for exploration or for well
development requires special engineering consid-
The water requirements and design capacity factors
eration and is costly.
for domestic, fire and other functional uses are
specified in TM 5-813-1/AFM 88-10, Volume 1.
3-3. Surface waters.
Both ground and surface waters are available in the
Arctic and Subarctic but the environmental condi-
Many shallow lakes and small streams freeze com-
tions require somewhat special approaches for their
pletely in the winter, eliminating them temporarily as
development. In addition, ice and snow are some-
a water source. Some installations pump water from
times used for water supply augmentation or as
such sources in the summer months and store the
emergency or stand-by sources.
winter supply. Larger streams and deep lakes can
have liquid remaining beneath the ice but the volume
3-2. Environmental constraints.
available is limited since there is no contribution
from precipitation in the winter. The large quantity
In most of the Arctic and Subarctic, precipitation is
of ice and snow results in major annual flows
light, terrain is relatively flat and runoff is concen-
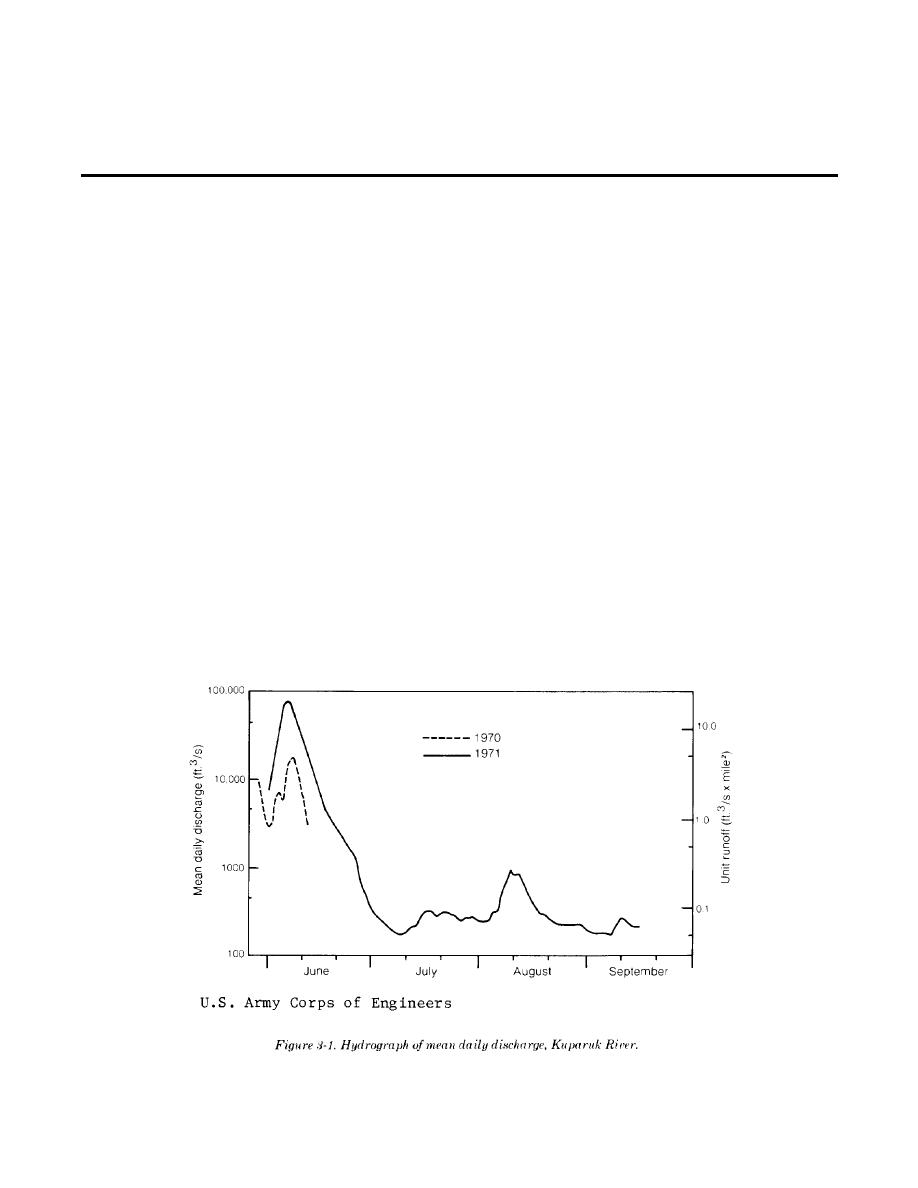
occurring during the spring "break-up." Figure 3-1
trated in the short period during ice breakup. There
shows a hydrograph for a typical medium-sized
are many small, shallow lakes and ponds and
arctic river.
numerous rivers and streams. Ice cover varies
a. Rivers. The volume of flow is low in the
according to local conditions but generally lasts
winter but water quality is excellent since sediment
from 6 to 10 months and approaches 6 feet in depth
transport from glacial sources is minimal and surface
in small quiescent water bodies (see paragraph 12-
runoff recharges do not occur. Winter water
9a for procedures to estimate thickness of ice for-
temperatures are very low (33 degrees F), which
mation). Hydrologic data for these regions are
creates difficulties for treatment, and intakes can
scarce so it is difficult to predict reliable yields.
clog due to formation of frazil ice. Floating ice
Permafrost is essentially impermeable so there is
during freezeup and breakup periods can damage or
little direct recharge of most aquifers. Any penetra-
3-1



 Previous Page
Previous Page
