TM 5-852-4/AFM 88-19, Chap. 4
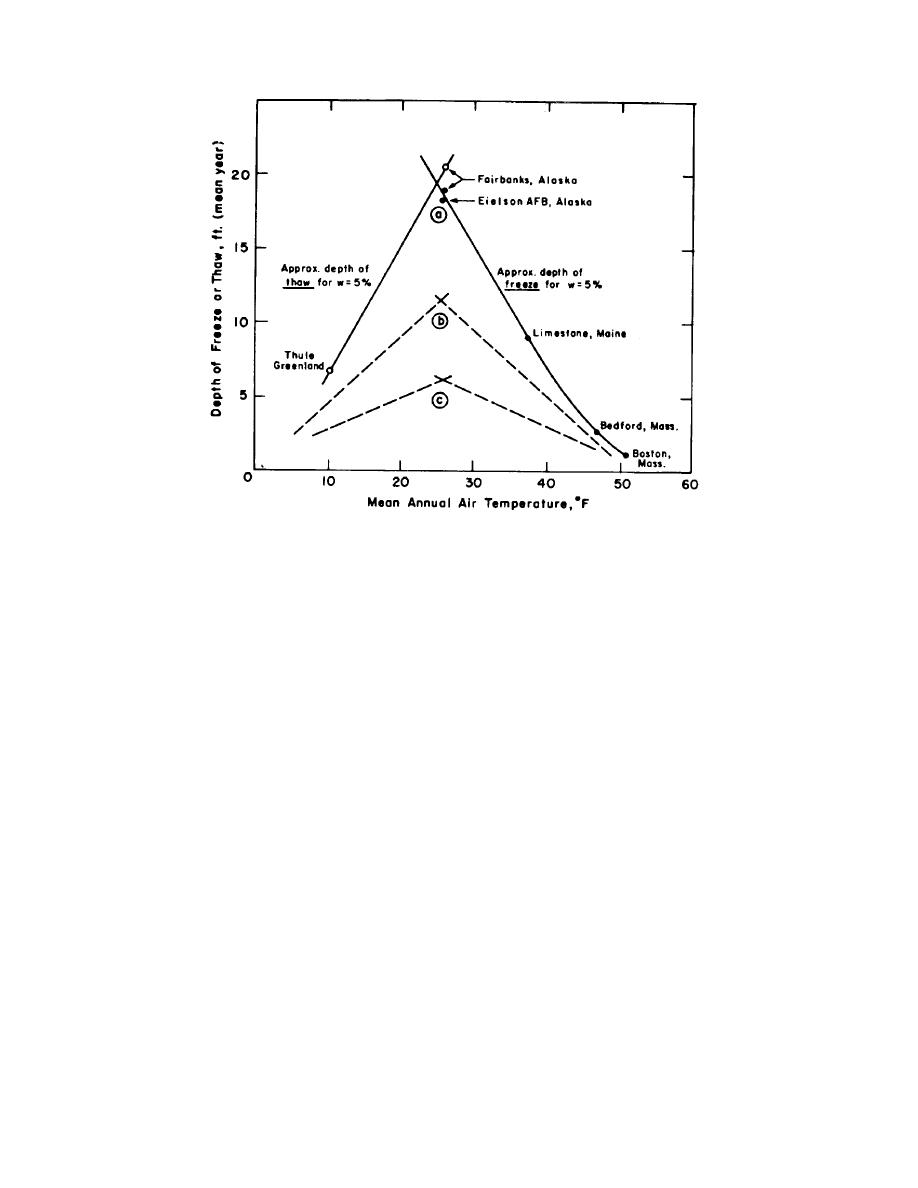
(a) For bituminous paved areas over well drained grovel, kept clear of snow.
(b) a (c) Typical for other soil, moisture and surface conditions.
U. S. Army Corps of Engineers
Figure 1-2. Freeze or thaw penetration vs mean annual temperature 164.
ground is absent only at a few widely scattered locations,
time behind the air temperature variations occurring at
197
the surface . The decrease of annual amplitude with
as at the bottom of lakes and rivers.
(b) In
zones
of
discontinuous
depth is illustrated in a more general way in figure 1-4.
permafrost, permafrost is found intermittently in various
Below a depth in the range of 30 to 60 feet, the
amplitude of annual temperature variation becomes
degrees. There may be discontinuities in both horizontal
small and the temperature gradient corresponding to the
and vertical extents.
normal flow of heat outward from the interior of the earth
(c) The boundaries between zones of
becomes discernible. When the ground temperature
continuous permafrost, discontinuous permafrost, and
curve with depth at its warmest extreme is below
seasonal frost without permafrost are poorly defined.
freezing over a portion of its length, as in figure 1-4, a
Distinctions between continuous and discontinuous
permafrost condition exists. When the curve shows
permafrost, in particular, are somewhat arbitrary.
ground temperatures entirely above freezing at its
(d) Definitions of specialized terms,
warmest extreme, but freezing does occur at its coldest
more detailed discussions on seasonal frost and
extreme, only seasonal frost conditions exist.
A
permafrost, and the approximate extent of continuous
seasonal freeze and thaw zone, called the "annual frost
and discontinuous permafrost in the Northern
zone," occurs even in the permafrost areas, except at
Hemisphere are given in TM 5-852-1 0 general
very extreme locations where the air temperatures
provisions.
remain well below freezing even in the summer. The
c. Thermal regime in the ground. As shown in
annual frost zone is usually not more than 10 feet thick,
figure 1-3, temperatures below the ground surface vary
but it may exceed 20 feet.
with the seasons. The annual ground temperature
fluctuation decreases in amplitude with depth and lags in
1-3



 Previous Page
Previous Page
