CEMP-ET
TI 809-53
01 May 1999
CHAPTER 10
COPPER AND OTHER CRAFTED METALS
REFERENCE
CEGS 07610 (Copper Roof Systems)
10-1. COPPER AND OTHER CRAFTED METALS.
a. Overview. Copper, lead-coated copper, terne coated steel (lead-tin alloy), terne-coated
stainless steel (TCS), zinc, and lead roofing are more formable and ductile than steel and aluminum
panels and are generally used in crafted systems where hand forming and/or soldering is required (Table
10-1). Most are extremely durable with records of roofs in service for centuries. These metals tend to be
relatively soft and are used in nonstructural applications where solid roof decking is used. Copper metal
gradually changes from a bright metallic copper color to brown, and eventually green (patina). In areas of
low air pollution (sulfur), lead, lead-coated copper and TCS may suffer from a red coloration (lead oxide)
rather than the expected dark gray patina. Because of their high material costs and intensive labor
requirements early historical uses of these metal roof systems were in cathedrals and civic buildings.
Typically, small flat pans with folded edges are formed. Cleats engage the folded-over edge of the pan
and are nailed to the substrate. The adjacent panel with a folded-under edge engages the installed pan
concealing the installed clip (figure 10-1). On low-slopes the seams are soldered together for
waterproofness. Crafted metal roofings are generally shop-fabricated by the contractor for each specific
application rather than factory formed. However, some automatic pan formers and mechanical seamers
are also used. Copper roofs include locked and soldered flat seam, standing seam, batten seam, and
custom design.
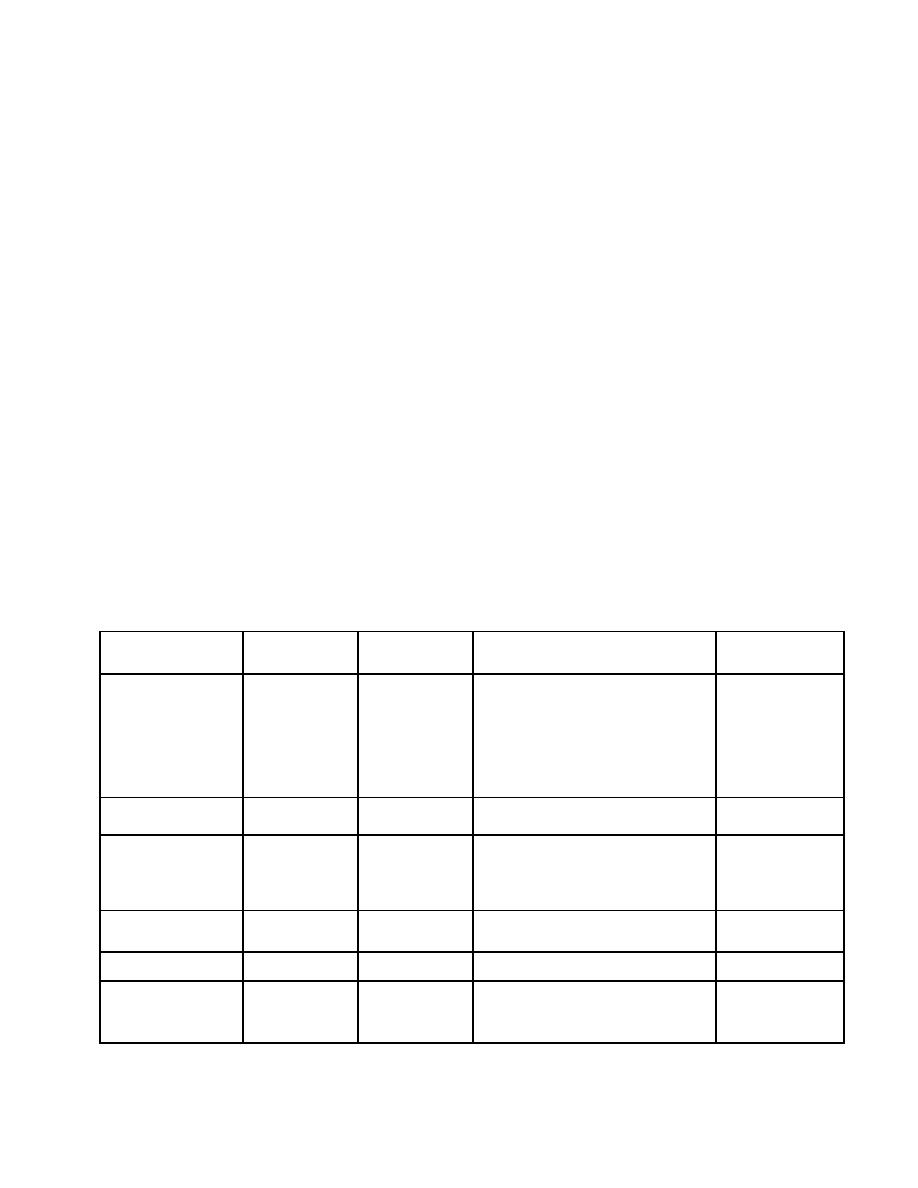
Table 10-1. Properties of Crafted Metals
Metal
Fastener
Ability to Solder,
Corrosion Resistance/Durability
Weathering
Compatibility
Weld, or Braze*
Characteristics of
Unfinished Material
Limestone, stucco, concrete, and other light
Copper
Copper, Brass, or
Solder-Yes
Brown tones
colored porous materials can show staining from
Stainless Steel
Weld-Yes
developing into a
moisture run-off from copper. Iron, galvanized
green-gray patina.
metal, and acidic solutions from some trees can
stain copper. Acid leaching from cedar roofing
can impede patina development and in severe
cases cause localized thinning of the copper.
Bitumen and fire-treated woods containing salt
are corrosive to copper. Copper should not be in
contact with steel or galvanized steel.
Used to avoid staining associated with copper.
Lead-Coated Copper
Copper, Brass, or
Solder-Yes
Dark gray to gray
However, lead oxide can cause staining (see
Stainless Steel
black.
"Lead" below).
Inert, atmospheric corrosion has little effect.
Lead
Copper, Brass, or
Solder-Yes
Dark gray to gray
Lead oxide can stain glass, stainless steel, and
Stainless Steel
Weld-Yes
black.
other materials. Lead is attacked by free lime
(found in fresh concrete). Lead can be stained
by rust from steel.
Do not nail through metal; use cleats. Avoid
Terne-Metal (Terne-
Stainless Steel
Dark gray.
Solder-Yes
contact with aluminum, copper or acidic
Cadmium Plated
Coated Carbon Steel)
materials. Must be painted.
or Galvanized
Does not stain.
Terne-Coated
Stainless Steel
Solder-Yes
Medium to dark gray.
Stainless Steel (TCS)
Not compatible with bituminous roofing materials.
Zinc
Galvanized or
Solder-Yes
Dark bluish gray.
Copper generates a corrosion compound that
Stainless Steel
attacks zinc. Sulfur dioxide inhibits the
development of zinc's carbonate film. Wood
preservatives can corrode zinc.
*When welding or brazing metal components, the gauge of the metal will affect the level of difficulty in achieving a proper weld (i.e.,
thicker materials are generally easier to weld or braze).
10-1



 Previous Page
Previous Page
