UFC 3-260-03
15 Apr 01
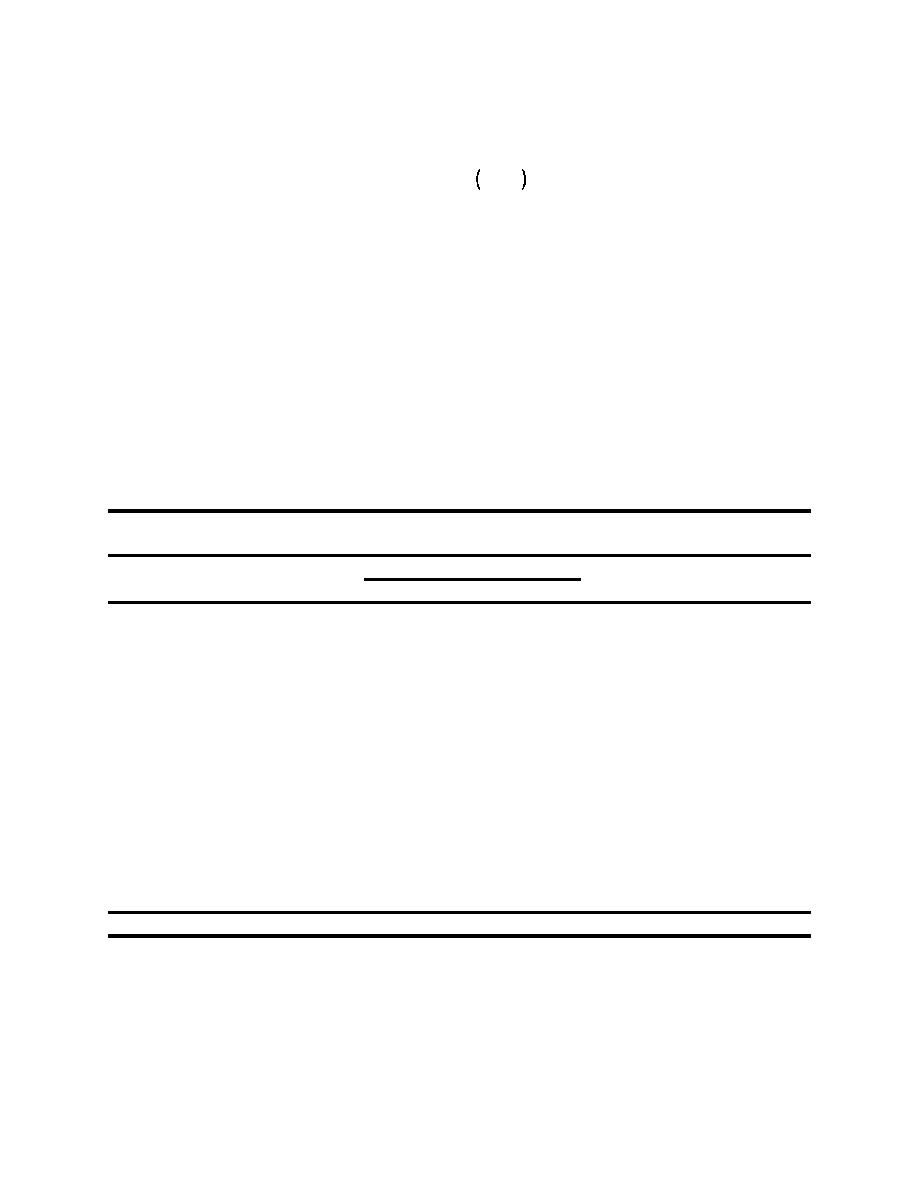
Deflection j ' Aji % Sji log Ei
(eq 4-2)
where
A = intercept
S = slope
j = 1 to the number of deflections
I = 1 to the number of layers with unknown modulus values
c. For WESDEF, a range of modulus values is input with an estimated initial modulus value for
each layer for which modulus values are to be determined. The number of unknown modulus values
cannot exceed the number of measured deflections. Best results are obtained when not more than three
layers are computed in a single execution.
d. Default ranges and initial estimates for the modulus and Poisson's ratio of pavement materials
are recommended in table 4-1.
Table 4-1
WESDEF Default Modulus Values, MPa (psi)
Range
Initial
Poisson's
Material
Minimum
Maximum
Estimate
Ratio
Asphalt concrete
689 (100,000)
13,780
2,411
0.35
(2,000,000)
(350,000)
Portland cement concrete
17,222
48,230
24,115
0.15
(2,500,000)
(7,000,000)
(3,500,000)
Resin Modified Pavement*
4,823
20,669
11,713
0.27
(700,000)
(3,000,000)
(1,700,000)
High-quality stabilized base
3,445
17,222
6,890
0.20
(500,000)
(2,500,000)
(1,000,000)
Base-subbase, stabilized
689
6,890
2,067
0.25
(100,000)
(1,000,000)
(300,000)
Base-subbase, unstabilized
34
1,033
207
0.35
(5,000)
(150,000)
(30,000)
Subgrade
6.9
344
103
0.40
(1,000)
(50,000)
(15,000)
* To be added to WESDEF later.
e. If the deflection basin includes a deflection measured at an offset distance of 1.83 meters
(72 inches), the initial subgrade modulus is estimated as follows:
E ' 59,304.82 (D72 )& 0.98737
(eq 4-3)
4-4



 Previous Page
Previous Page
