Chapter 6
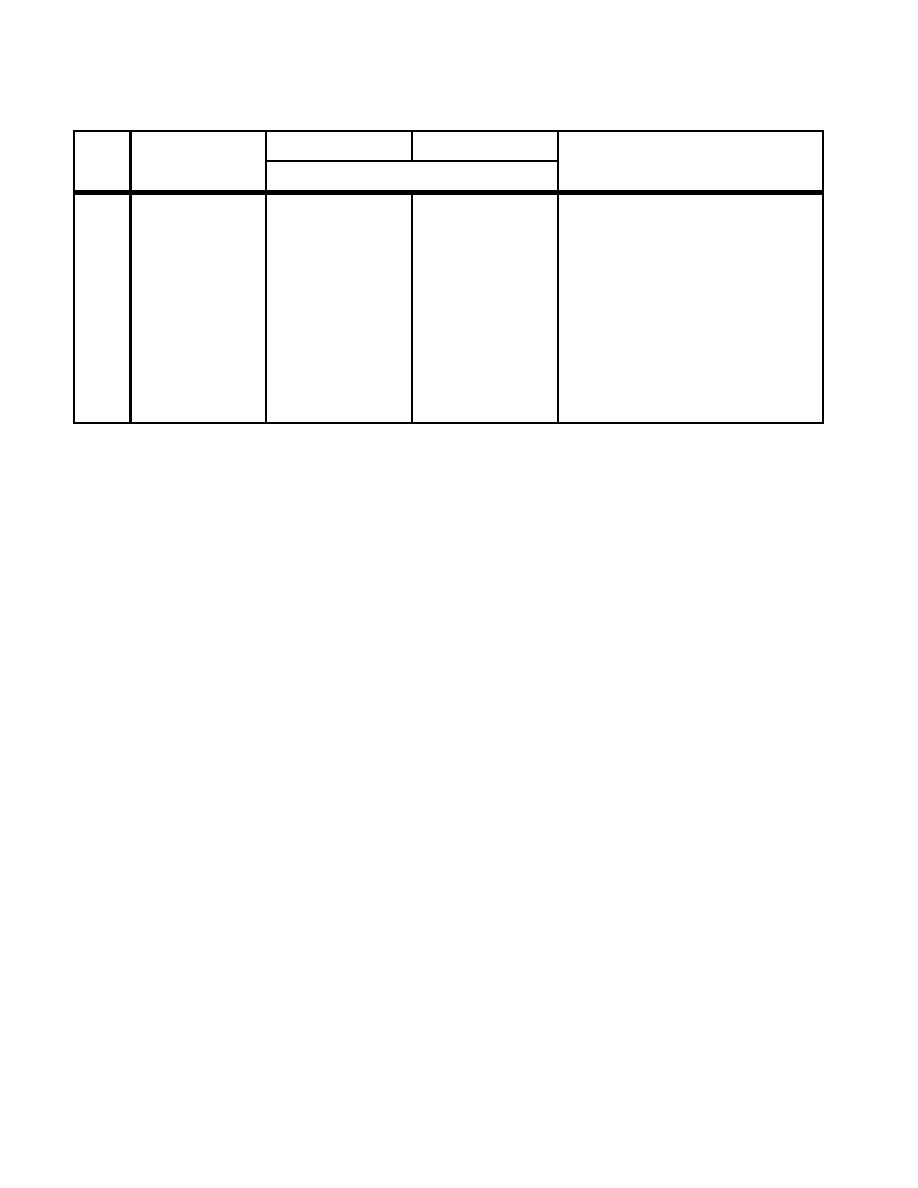
Table 6.1. Fixed-Wing Aprons.
Class A Runway
Class B Runway
Item
Item
No.
Description
Requirement
Remarks
(a) 40 mm [1-"]
Grades in
16
Max 10.0%
drop off at edge
Cleared Area
of paved
Beyond
shoulder.
Shoulders to
(b) 5% slope first
Fixed or Mobile
3 m [10 ft] from
paved shoulder.
(c) Beyond 3 m
[10 ft] from the
edge of the paved
shoulder, 10%.
Notes:
1. Wingtip clearances may be reduced to those allowed by AFI 11-218, Aircraft Operation and Movement on the
Ground, with a waiver.
2. Metric units apply to new airfield construction, and where practical modifications to existing airfields and
heliports, as discussed in Paragraph 1.4.4.
3. The criteria in this manual are based on aircraft specific requirements and are not direct conversions from
inch-pound (English) dimensions. Inch-pound units are included only as a reference to the previous standard.
4. Airfield and heliport imaginary surfaces and safe wingtip clearance dimensions are shown as a direct
conversion from inch-pound to SI units.
6.6. Taxiing Characteristics on Aprons for Fixed-Wing Aircraft:
6.6.1. Apron Taxilanes. Taxi routes across parking aprons, referred to as taxilanes, are marked on
the apron for safe passage of the aircraft. Typical taxilane locations are illustrated in Figures 6.1 and
6.4. Minimum wingtip clearances between parked and taxiing aircraft are shown in Table 6.1. (See
Figure 6.2.) AFI 11-218 provides authorization for operation of aircraft at reduced clearances under
certain circumstances. If a decision is made to reduce clearances based upon this authorization, you
must waive the safe clearance requirements provided within this chapter in accordance with
Attachment 2.
6.6.2. Turning Capabilities (Aircraft Turning and Maneuvering Characteristics). Army ETL 1110-
3-394, Aircraft Characteristics for Airfield-Heliport Design and Evaluation, provides sources for
obtaining various turning diagrams for U.S. Army, Air Force, and numerous civil and commercial
fixed wing aircraft.
6.6.3. Departure Sequencing. Egress patterns from aircraft parking positions to taxiways should be
established to prevent congestion at the apron exits.
6.6.4. See USAF Engineering Technical Letter 01-5, Jet Engine Thrust Standoff Requirements for
Airfield Asphalt Edge Pavements, and Attachment 8 for information on minimum standoff distances
from edge pavements.
6.7. Parking Apron for Rotary-Wing Aircraft. Mass parking of rotary-wing aircraft will require an
apron designated for rotary-wing aircraft. Parking for transient rotary-wing aircraft and at aviation
facilities where only a few rotary-wing aircraft are assigned, may be located on aprons for fixed-wing
6-11



 Previous Page
Previous Page
