Chapter 4
4.12. Imaginary Surfaces for Rotary-Wing Runways, Helipads, Landing Lanes and Hoverpoints.
Rotary-wing runways, helipads, landing lanes, and hoverpoints have imaginary surfaces similar to the
imaginary surfaces for fixed-wing facilities. The imaginary surfaces are defined planes in space which
establish clearance requirements for helicopter operations. An object, either manmade or natural, which
projects through an imaginary surface plane is an obstruction to air navigation. Layout of the rotary-wing
airspace imaginary surfaces are shown in Tables 4.7 and 4.8 and Figures 4.1 through 4.10. Rotary-wing
airspace imaginary surfaces are defined in the glossary and summarized below:
4.12.1. Primary Surface.
4.12.2. Approach-Departure Clearance Surface (VFR).
4.12.3. Approach-Departure Clearance Surface (VFR Limited Use Helipads).
4.12.4. Approach-Departure Clearance Surface (IFR).
4.12.5. Horizontal Surface (IFR).
4.12.6. Transitional Surfaces.
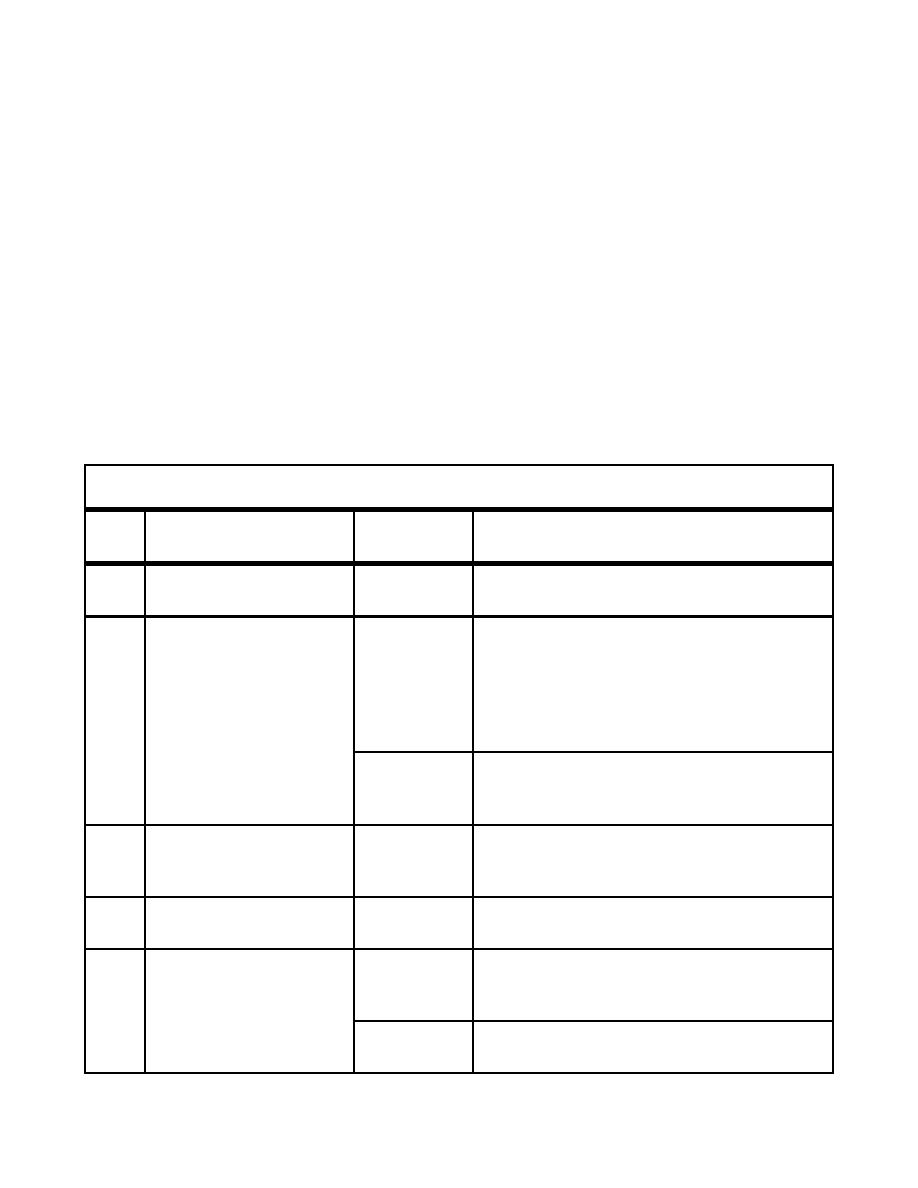
Table 4.6. Rotary-Wing Runway and Landing Lane Clear Zone and Accident Potential Zone (APZ).
(See Notes 1 and 2.)
Item Description
Requirement
Remarks
No.
1
121.92 m
Clear Zone Length
Clear Zone begins at the end of the primary
[400 ft]
surface.
91.44 m
VFR rotary wing runways and landing lanes.
2
Clear ZoneWidth
[300 ft]
(center width on extended
See Note 2.
runway/landing lane
centerline)
(corresponds to the width
of the primary surface)
228.60 m
IFR rotary-wing runways and landing lanes.
[750 ft]
See Note 2.
2.0% Min.
Clear Zone only.
3
Grades in Clear Zone
5.0% Max.
Area to be free of obstructions. Rough grade
in Any Direction
and turf when required.
4
243.84 m
See Notes 2 and 3.
APZ I Length
[800 ft]
5
91.44 m
VFR rotary wing runways and landing lanes.
APZ I Width
[300 ft]
See Notes 2 and 3.
228.60 m
IFR Rotary-Wing Runways and Landing Lanes.
[750 ft]
4-24



 Previous Page
Previous Page
