Chapter 4
ROTARY-WING RUNWAYS, HELIPADS, LANDING LANES, AND HOVERPOINTS
4.1. Contents. This chapter presents design standards and requirements for rotary-wing (helicopter)
landing facilities: runways, helipads, helicopter landing lanes, and hoverpoints.
4.2. Landing and Take-off Layout Requirements. The landing design requirements for rotary-wing
landing facilities, which include rotary-wing runways, helipads, landing lanes, slide areas (autorotation
lanes), and hoverpoints, are similar to the requirements for fixed-wing runways, as discussed in Chapter 3.
4.3. Rotary-Wing Runway. The rotary-wing runway allows for a helicopter to quickly land and roll to a
stop, compared to the hovering stop used during a vertical helipad approach.
4.3.1. Orientation and Designation. Consider the strength, direction, and frequency of the local winds
when orienting a runway to minimize cross winds. Follow the methods for fixed-wing runways
presented in Chapter 3. Runways are identified by the whole number, nearest one-tenth (1/10), of the
magnetic azimuth of the runway centerline when viewed from the direction of approach.
4.3.2. Dimensions. Table 4.1 presents dimensional criteria for the layout and design of rotary-wing
runways.
4.3.3. Layout. Layout for rotary-wing runways, including clear zones, are illustrated in Figure 4.1 for
VFR runways and Figures 4.2 and 4.3 for IFR runways.
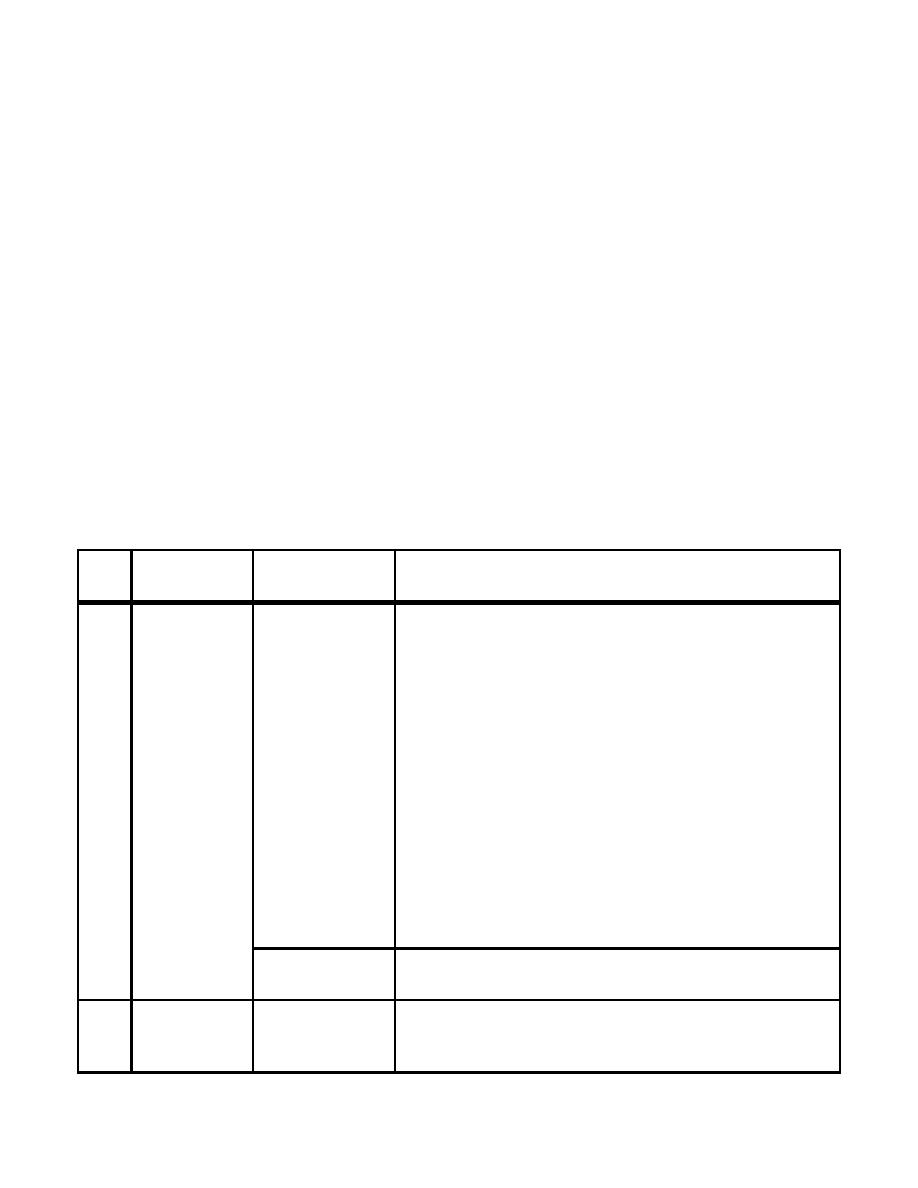
Table 4.1. Rotary-Wing Runways.
Item
Item
Description
Requirement
Remarks
No.
For Army and Air Force facilities, use basic length up to
1
Basic Length
490 m
1,220 meters [4,000 feet] in elevation above Mean Sea Level
[1,600 ft]
(MSL). Increase basic length to 610 meters [2,000 feet]
when above 1,220 meters [4,000 feet] in elevation above
MSL.
For Navy and Marine Corps facilities, basic length to be
corrected for elevation and temperature. Increase 10% for
each 300 m [1,000 ft] in elevation above 600 m [2,000 ft]
MSL and add 4.0% for each 5C [10F], above 15C [59F]
for the average daily maximum temperature for the hottest
month.
For a special mission or proficiency training such as
autorotation operations, the length may be increased up to
300 meters [1,000 feet]; in which case, make no additive
corrections.
137.2 m
For facilities constructed prior to publication of this
(450 ft)
manual.
2
Width
23 m
For Navy and Marine Corps facilities, increase width to 30
[75 ft]
meters [100 feet] on runways which regularly
accommodate H-53.
4-1



 Previous Page
Previous Page
