TM 5-822-5/AFM 88-7, Chap. 1
c. Design method. The design method permits a
(2) From figure 18-3, determine frost
small amount of frost penetration into frost-sus-
penetration depth (a). These frost penetration
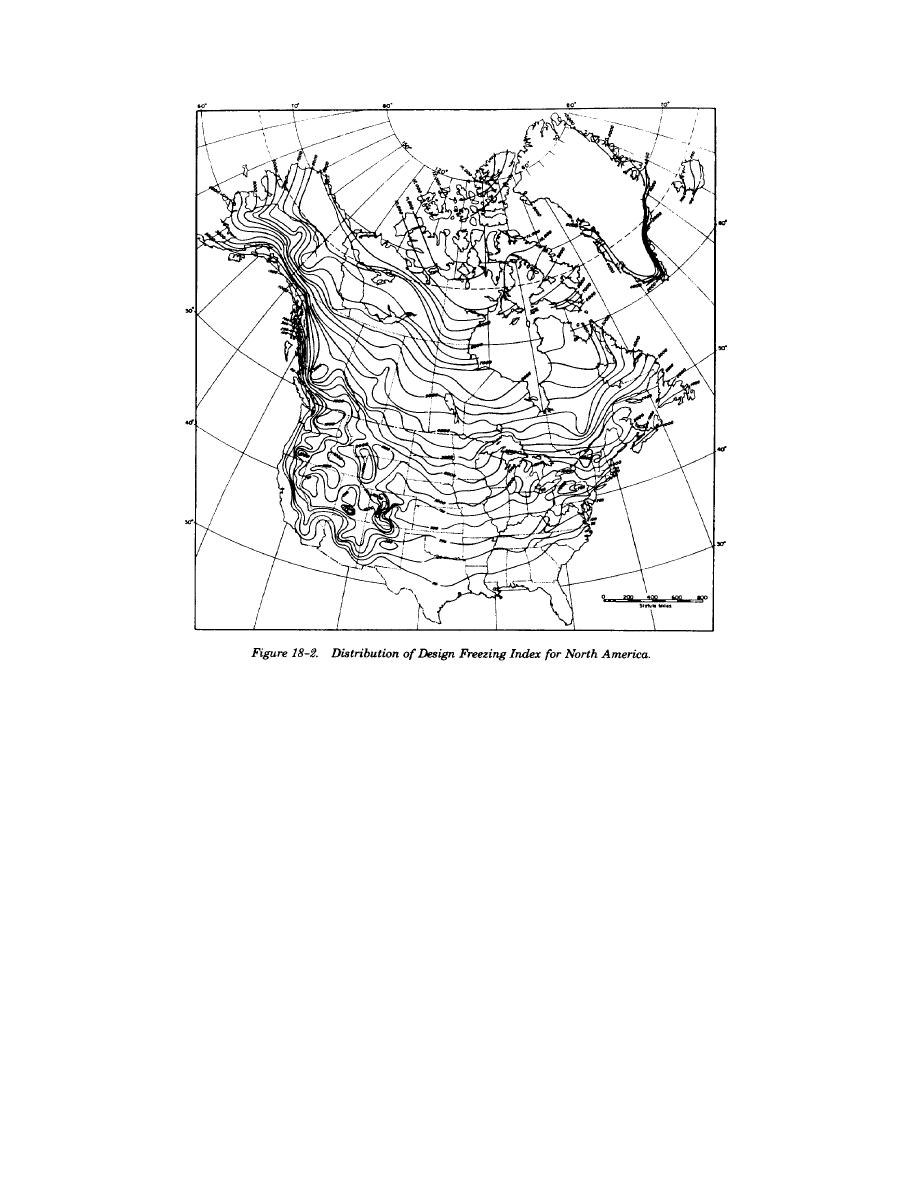
ceptible subgrades for the design freezing index
depths are based on modified Berggren formula and
year. The procedure is described in the following
computational procedures outlined in TM 5-852-6.
subparagraphs.
Frost penetration depths are measured from
(1) Estimate average moisture contents in
pavement surface. Depths are computed on a 12-
the base course and subgrade at start of freezing
inch rigid pavement kept free of snow and ice, and
period, and estimate the dry unit weight of base.
are good approximations for bituminous pavements
The moisture content of the base is generally af-
over 6 to 9 inches of high-quality base.
fected by the moisture content of the subgrade,
Computations also assume that all soil beneath
drainage, precipitation, and depth to water table. As
pavements within depths of frost penetration are
the base course may, in some cases, comprise
granular and non-frost susceptible. It was assumed
successive layers containing substantially different
in computations that all soil moisture freezes at 32
fine contents, the average moisture content and dry
degrees Fahrenheit. Use straight line interpolation
unit weight should he weighted in proportion to the
where necessary. For rigid pavements greater than
thickness of the various layers. Alternatively, if
12 inches thick, deduct 10 degree-days for each
layers of bound base course and granular unbound
inch of pavement exceeding 12 inches from the
base course are used in the pavement, the average
design freezing index before entering figure 18-3 to
may be assumed to be equal to the moisture content
determine frost penetration depth (a). Then add
and dry unit weight of the material in the granular
extra concrete pavement thickness to the
unbound base course.
determined frost penetration.
18-8



 Previous Page
Previous Page
