TM 5-822-5/AFM 88-7, Chap. 1
pavement and base of 6 inches (2 inches of
pavement and 4 inches of base). Therefore, the
section using materials 1 and 2 will consist of a 4.5-
inch subbase course of material 1, a 4-inch base
course of material 2, and a 2-inch pavement.
8-6. Thickness Criteria-Stabilized Soil Layers.
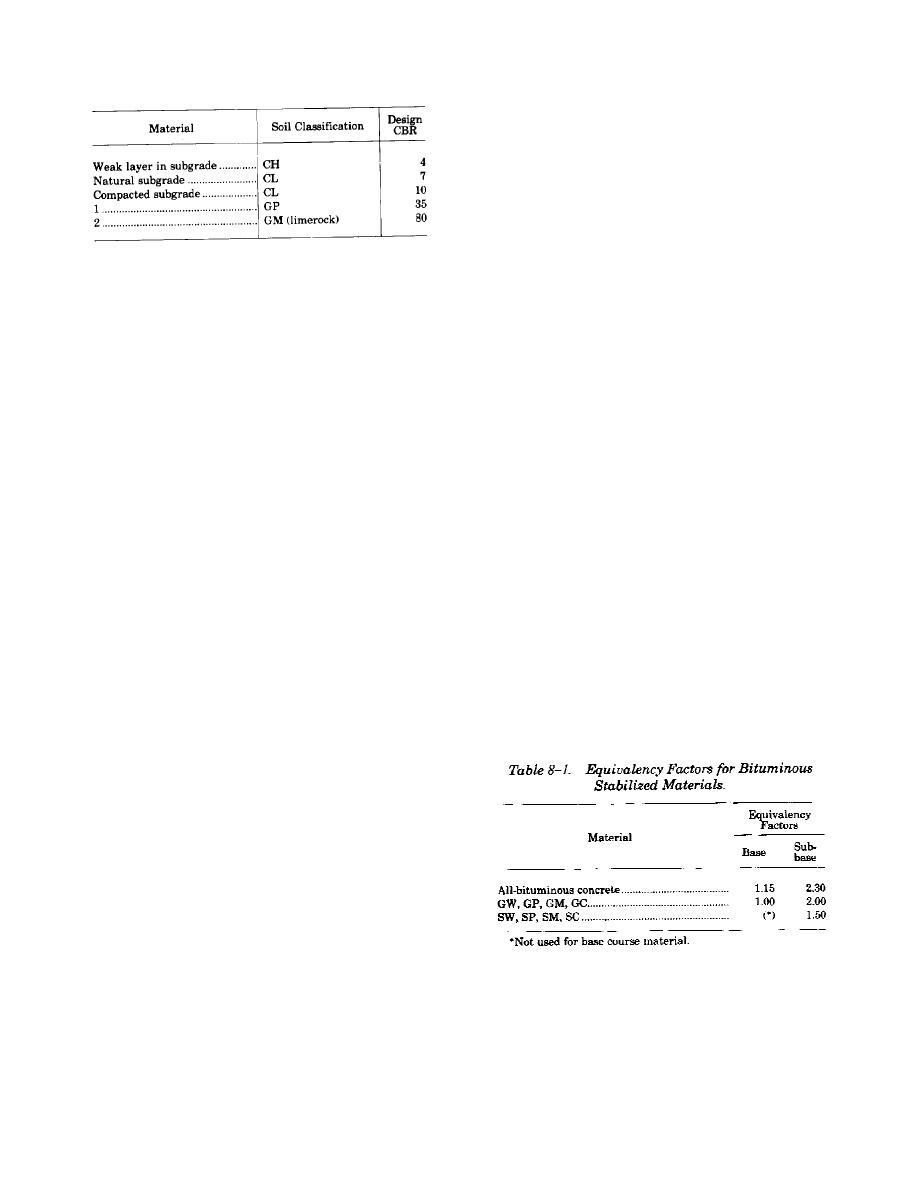
a. Equivalency factors. The use of stabilized soil
layers within a flexible pavement provides the op-
portunity to reduce the overall thickness of pave-
The total thickness and thicknesses of the various
ment structure required to support a given load. To
subbase and base layers are determined as follows:
design a pavement containing stabilized soil layers
a. Total thickness. The total thickness of sub-
requires the application of equivalency factors to a
base, base, and pavement will be governed by the
layer or layers of a conventionally designed
CBR of the compacted subgrade. From the flexible-
pavement. To qualify for application of equivalency
pavement design curves shown in figure 8-1, the
factors, the stabilized layer must meet appropriate
required total thickness above the compacted sub-
strength and durability requirements set forth in TM
grade (CBR of 10) is 11 inches. A check must be
5-822-4. An equivalency factor represents the
made of the adequacy of the strength of the un-
number of inches of a conventional base or subbase
compacted subgrade and of the weak layer within
which can be replaced by 1 inch of stabilized
the subgrade. From the curves in figure 8-1, the
material. Equivalency factors are determined as
required cover for these two layers is 14.5 and 21
shown in table 8-1 for bituminous stabilized
inches, respectively. If the design thickness is 11
materials, and from figure 8-2 for materials
inches and the subgrade is compacted to 9 inches
stabilized with cement, lime, or a combination of
below the subgrade surface, the natural subgrade
flyash mixed with cement or lime. Selection of an
will be covered by a total of 20 inches of higher
equivalency factor from the tabulation is dependent
strength material. Similarly, the soft layer occurring
upon the classification of the soil to be stabilized.
24 inches below the subgrade surface will be
Selection of an equivalency factor from figure 8-2
protected by 35 inches of total cover. Thus, the
requires that the unconfined compressive strength
cover is adequate in both cases.
as determined in accordance with ASTM D 1633 be
b. Minimum base and pavement thicknesses. For
known. Equivalency factors are determined from
a design index of 5 the minimum base thickness is 4
figure 8-2 for subbase materials only. The
inches and the pavement thickness is 2 inches as
relationship established between a base and subbase
indicated in table 6-1. If, however, the CBR of the
is 2 to 1. Therefore, to determine an equivalency
base material had been 100 rather than 80, a
factor for a stabilized base course, divide the
minimum pavement thickness of 2 inches would
subbase factor from figure 8-2 by 2.
have been required.
c. Thickness of subbase and base courses. The
design thickness of each layer of materials 1 and 2
will depend upon the CBR design value of each
material. The total thickness of subbase, base, and
pavement, as determined above, is 11 inches. The
thickness required above material 1 (CBR = 35), as
determined from figure 8-1, is 3 inches; there- fore,
the required thickness of material 1 is 8 inches (11 -
3 inches). The 3-inch layer required above material
1 will be composed of material 2 and pavement;
however, adjustments must be made in the
thicknesses of material 2 and the pavement to
conform with minimum base and pavement
thickness, which is a combined thick-ness of
8-3



 Previous Page
Previous Page
