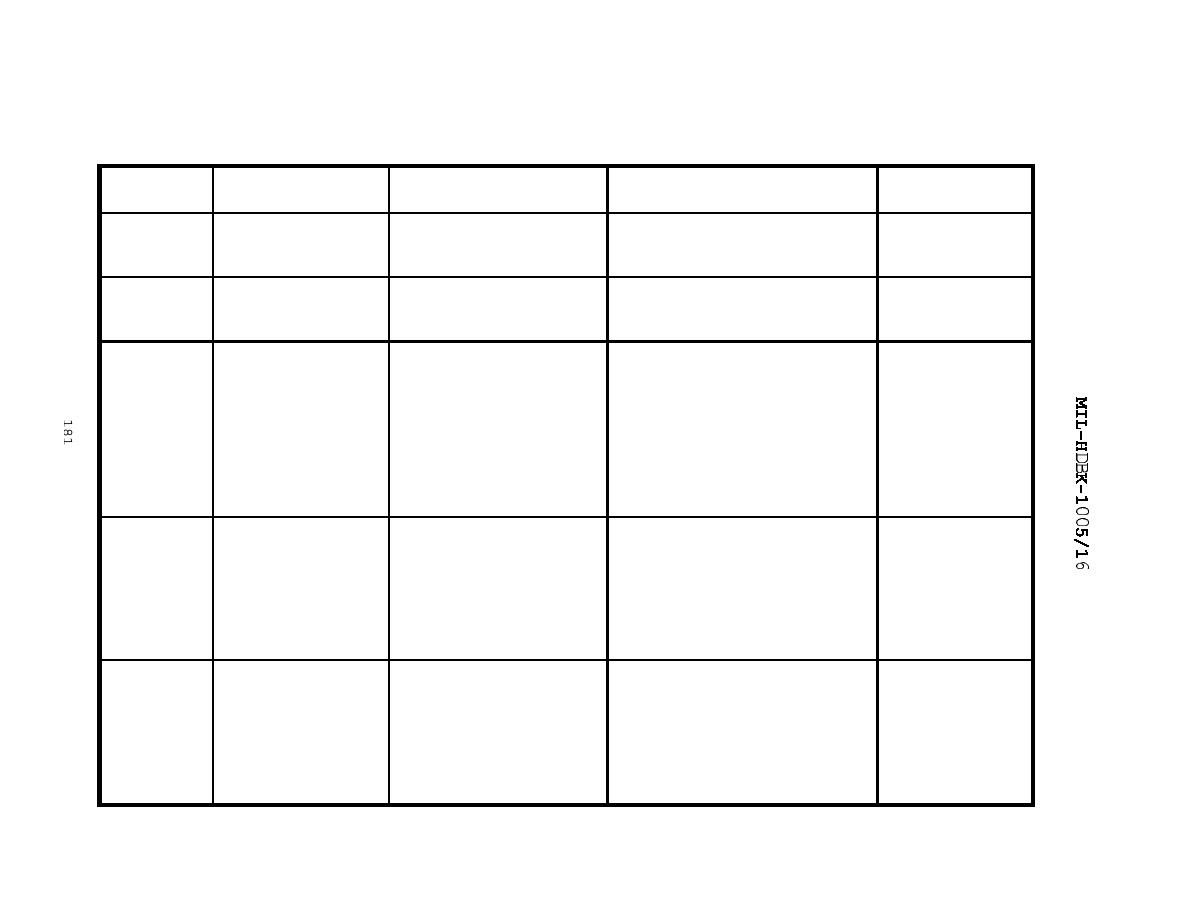
Table 18
Compositing Methods
Sample
Compositing
Mode
Principle
Advantages
Disadvantages
Comments
Continuous
Constant pumping
Minimal manual effort;
Requires large sample
Practical but
rate
requires no flow
capacity; may not be
not widely used
measurement
representative for highly
variable flows.
Continuous
Sample pumping
Most representative
Requires accurate flow
Not widely used
rate proportional
especially for highly
measurement equipment, large
to stream flow
variable flows;
sample volume, variable
minimal manual effort
pumping capacity, and power.
Periodic
Constant sample
Minimal
May not be representative,
Widely used in
volume; constant
instrumentation and
especially for highly
both automatic
time interval
manual effort;
variable flows.
samplers and
between samples
requires no flow
manual sampling
measurement
Periodic
Constant sample
Minimal manual effort
Requires accurate flow
Widely used in
volume; time
measurement/ reading
automatic as
interval between
equipment. Manual
well as manual
samples
compositing from flowchart.
sampling
proportional to
stream flow
Periodic
Constant time
Minimal
Manual compositing from flow
Used in
interval between
chart; in absence of prior
automatic
samples; sample
information on the ratio of
samplers and
volume
minimum to maximum flow,
widely used as
proportional to
there is a chance of
manual method
total stream flow
collecting either too small
at time of
or too large individual
sampling
discrete samples for a given
composite volume.
Periodic
Constant time
Minimal
Manual compositing from flow
Not widely used
interval between
chart. In absence of prior
in automatic
samples; sample
information on the ratio of
samplers but
volume
minimum to maximum flow,
may be done
proportional to
there is a chance of
manually
total stream flow
collecting either too small
since last sample
or too large individual
discrete samples for a given
composite volume.



 Previous Page
Previous Page
