UFC 3-220-01N
15 AUGUST 2005
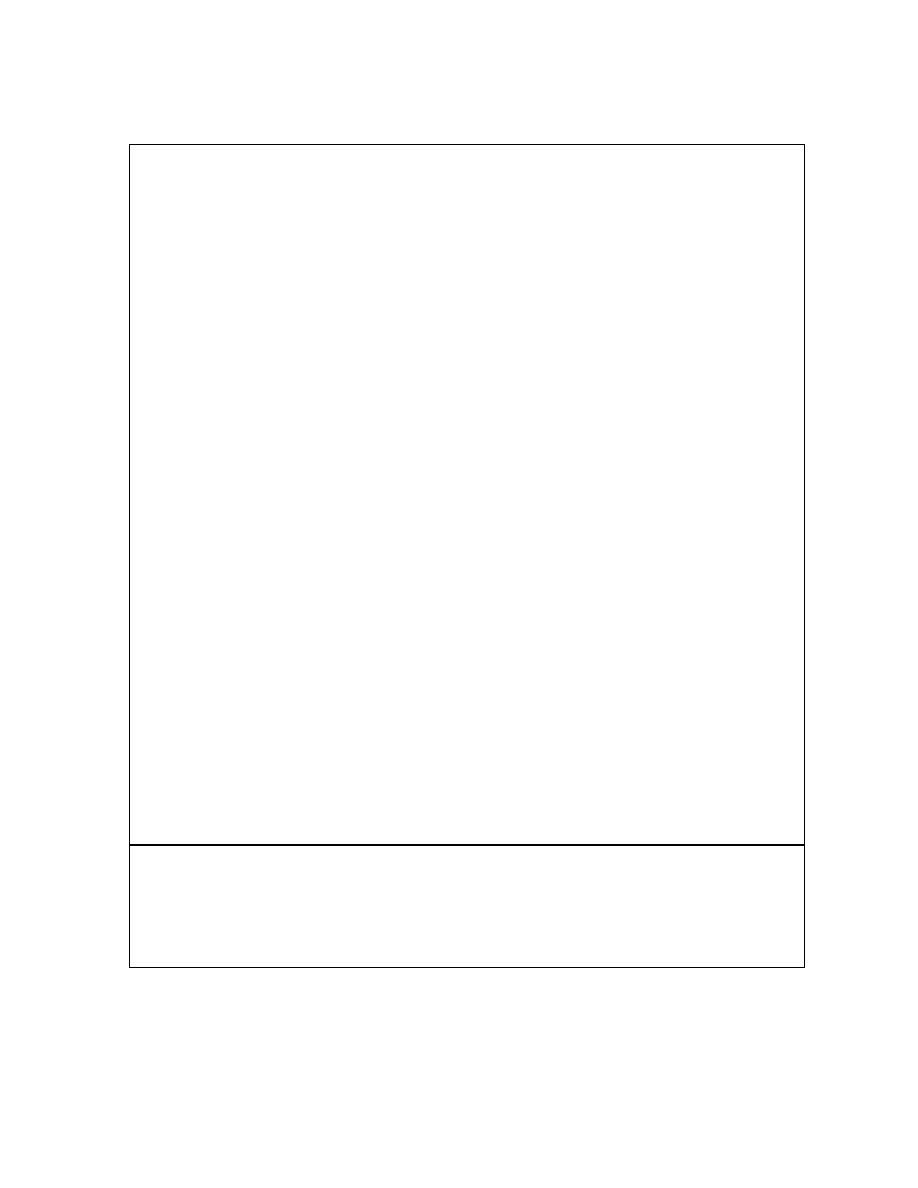
Table 12-6 Criteria for Excluding Need for Detailed Liquefaction Analyses
1. CL, CH, SC or GC Soils
2. GW or GP soils or materials consisting of cobbles, boulders, uniform rock
fill, which have a free-draining boundaries that are large enough to
preclude the development of excess pore properties
3. SP, SW or SM soils that have an average density equal to or greater than
85 percent, provided that the minimum relative density is not less than 80
percent
4. ML or SM soils in which the dry density is equal to or greater than 95
percent of the modified Proctor (ASTM D 1557) density
5. Soils of pre-Holocene age, with natural over consolidation ratio equall to or
greater than 16 and with relative density greater than 70 percent
6. Soils located above the highest potential groundwater table
7. Sands in which the N value is greater than three times the depth in feet, or
greater than 75; provided that 75 percent of the values meet this criterion,
the minimum N value is not less than one times the depth in feet, that there
are no consistent patterns of low values in definable zones or layers, and
that the maximum particle size is not greater than one inch. Large gravel
particles may affect N values so that the results of the SPT are not reliable
8. Soils in which the shear wave velocity is equal to or greater than 2000 fps.
Geophysical survey data and site geology should be reviewed in detail to
verify that the possibility of included zones of low velocity is precluded
9. Soils that, in undrained cycle triaxial tests, under isotropically consolidated,
stress controlled conditions, and with cyclic stress ratios equal to or greater
than 0.45, reach 50 or more with peak-to-peak strains not greater than 5
percent; provided that methods of specimem preparation and testing
conform to specified guidelines
Note: The criteria given above do not include a provision for exclusion of soils on
the basis of grain size distribution, and, in general, grain size distribution
alone cannot be used to conclude that soils will not liquefy. Under adverse
conditions non-plastic soils with a very wide range grain sizes may be
subject to liquefaction.
12-1.7
Seismic Effects on Foundations. Ground motions from earthquakes
cause motions of foundations by introducing forces at the foundation-soil contact
zone. Methods for estimating ground motions and their effects on the design of
foundation elements are discussed in UFC 3-220-10N.
12-25



 Previous Page
Previous Page
