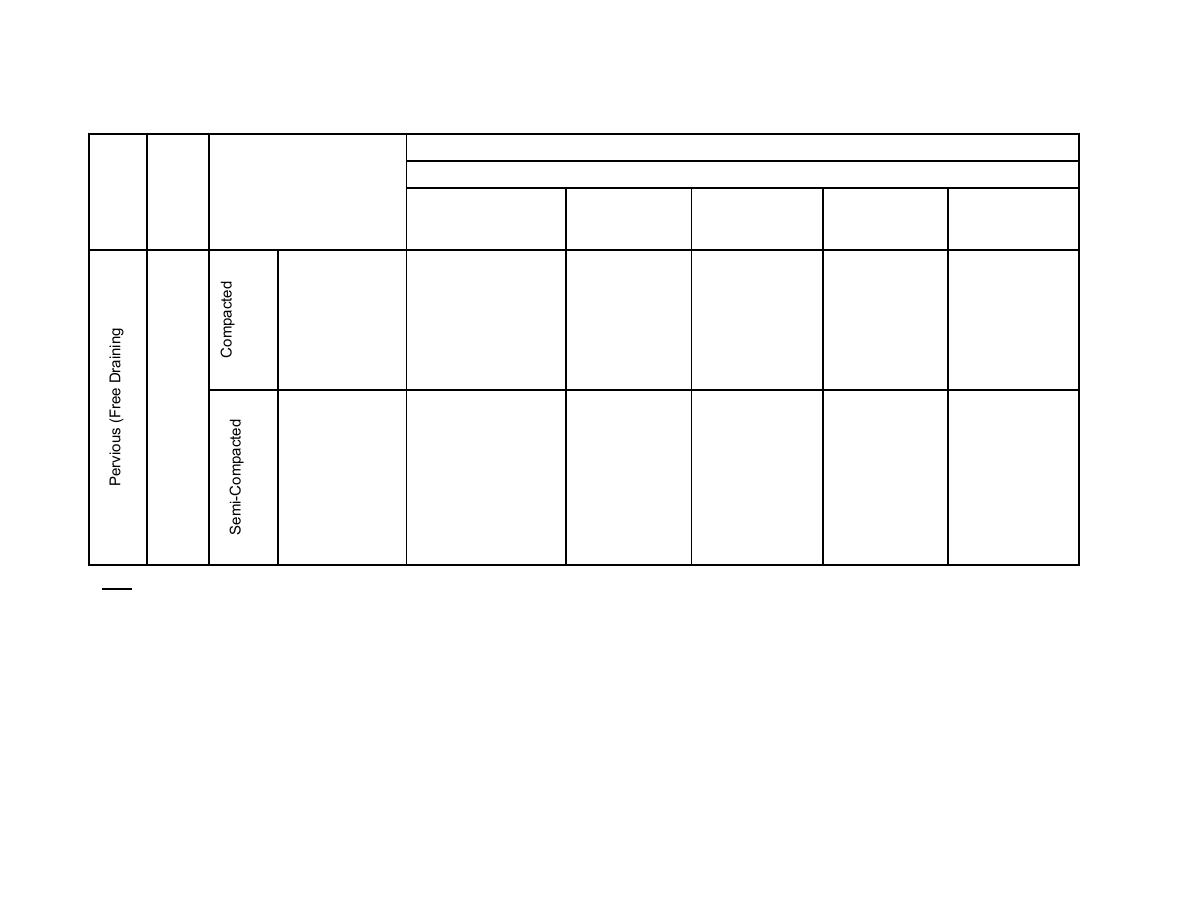
Table 8-5.1 Summary of Compaction Criteriaa
Fill and Backfill
Typical Equipment and Procedures for Compaction
Soil
Soil
Degree of Compaction
Equipment
No. of Passes
Comp. Lift
Placement
Field Control
Group
Types
or Coverages
Thickness mm
Water Content
(in)
GW
90 95% of CE
Vibratory Rollers
Indefinite
Indefinite
Saturate by
Control tests at
55 maximum
intervals to
Rubber Tired Rollerb
GP
2-5 Coverages
300 (12)
density
determine
degree of
SW
Crawler Type
2-5 Coverages
200 (8)
75 85% of
Tractorc
compaction or
relative density
SP
Indefinite
150 (6)
relative density
Power Hand
Tamperd
Rubber Tired Rollerb
85 to 90% of CE
2-5 Coverages
360 (14)
Saturate by
Control tests at
55 maximum
intervals to
Crawler Type
1-2 Coverages
250 (10)
density
determine
Tractorc
degree of
Indefinite
200 (8)
65 to 75% of
compaction or
Power Hand
relative density
Indefinite
200250 (8-10)
Tamperd
relative density,
if needed
Controlled routing of
construction
equipment
Note: The above requirements will be adequate in most construction venues. In special cases where tolerable settlements are unusually small, it may be necessary to
employ additional compaction equivalents to 95-100% of compaction effort. A coverage consists of one application of the wheel of a rubber tired roller or the treads of a
crawler type tractor over each point in the area being compacted. For a sheepsfoot roller , one pass consists of one movement of a sheepsfoot roller drum over the area
being compacted.
a)
From TM 5-818-1
b)
Rubber tired rollers having a wheel load between 80 and 111 kN (18,000 and 25,000 lb) with a tire pressure between 552-689 kPa (80-100 psi).
c)
Crawler type tractors weighing not < 89 kN (20,000 lbs) / exerting a foot pressure not < 4.5 kPa (6.5psi).
d)
Power hand tampers weighing more than 0.44 kN (100 lbs) / pneumatic or gasoline powered.
e) Sheepsfoot roller with a foot pressure between 1724-3448 kPa (250-500 psi)/ tamping feet 180-250 mm (7-10 in) long/ face area between 4500-10300 mm2
(7-16 sq. in. )



 Previous Page
Previous Page
