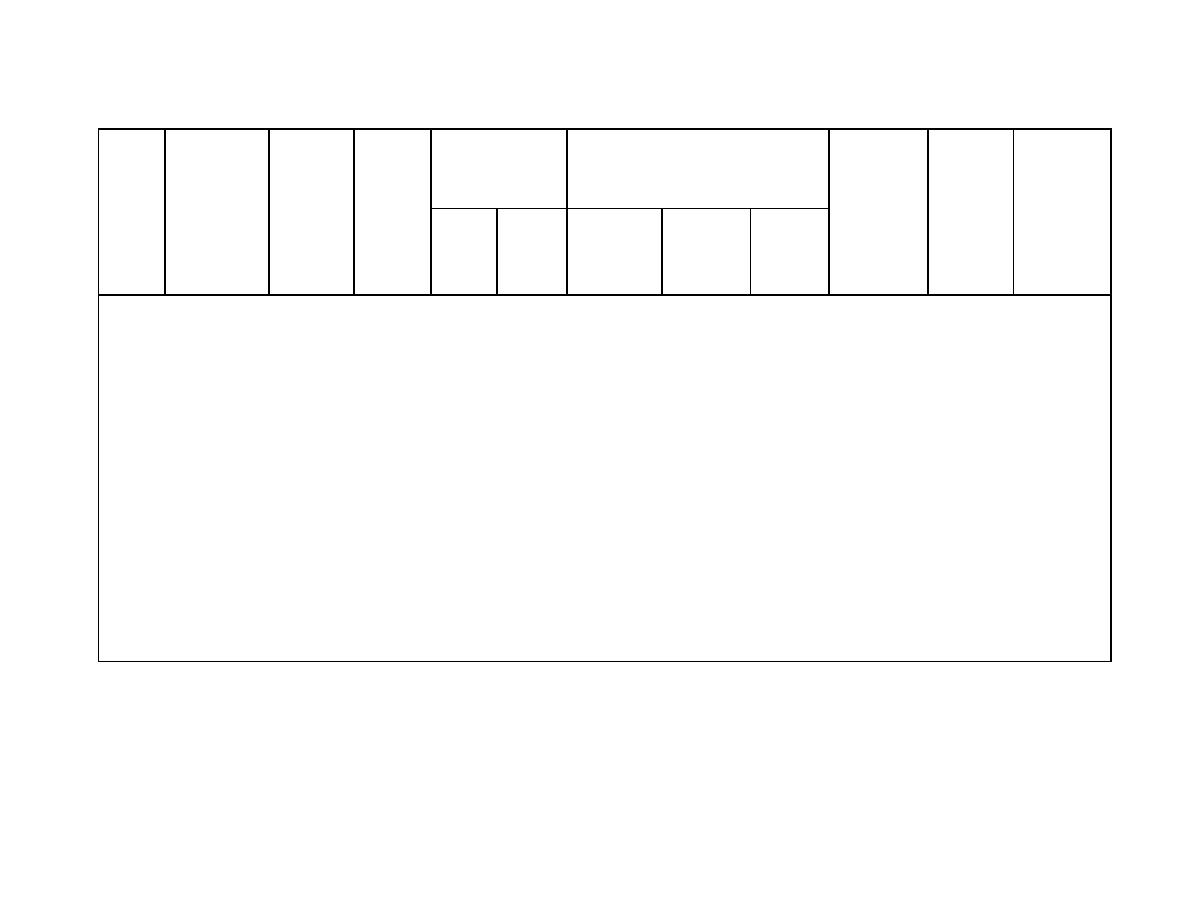
Table 8-3.1 Typical Engineering Properties of Compacted Materialsa
Typical Value of
Compression
(Percent of
Original Height)
Range of
Typical Strength Characteristics
Range of
Typical
Range of
Range of
Maximum
Optimum
Coefficient
CBR
Subgrade
At 138
At 345
Cohesion
Cohesion
Effective
Dry Unit
Water,
of
Values
Modulus k
kPa
kPa
(as
(saturated)
Stress
Weight,
Content
Permeability
kPa/mm
Group
Soil Type
(20
(50 psi)
compacted)
kPa (psf)
Envelope
gm/cm3
Percent
cm/sec
(lb/cu in)
Symbol
psi)
kPa (psf)
deg
(pcf)
(ft/min)
5 x 10-8
CL
Inorganic
15 or <
14-54
1.52-1.92
34-12
1.3
2.5
86 (1800)
13 (270)
28
(10-7)
clays of low
(50-200)
(95-120)
to medium
OL
Organic silts
1.28-1.60
33-21
-----
-----
-----
-----
-----
-----
5 or <
14-27 (50-
and silt-clays
(80-100)
100)
of low
2.5 x 10-7
MH
Inorganic
10 or <
14-27
1.20-1.52
40-24
2.0
3.8
72 (1500)
20 (420)
25
(5x10-7)
clayey silts,
(50-100)
(75-95)
elastic silts
5 x 10-8
CH
Inorganic
15 or <
14-34
1.28-1.68
36-19
2.6
3.9
103 (2150)
11 (230)
19
(10-7)
clays of high
(50-150)
(80-105)
OH
Organic and
1.20-1.60
45-21
-----
-----
-----
-----
-----
-----
5 or <
7-27
silty clays
(75-100)
(25-100)
Notes: 1. All properties are for condition of Standard Proctor maximum density except values of k and CBR, which are for CE55 maximum density.
2. Typical strength characteristics are for effective strength envelopes and are obtained from USBR data.
3. Compression values are for vertical loading with complete lateral reinforcement.
4. (>) Indicates that typical property is greater than the value shown. (.....) Indicates insufficient data available for an estimate.



 Previous Page
Previous Page
