TM 5-852-5/AFR 88-19, Volume 5
low as 35 degrees F. The temperature of wastewater
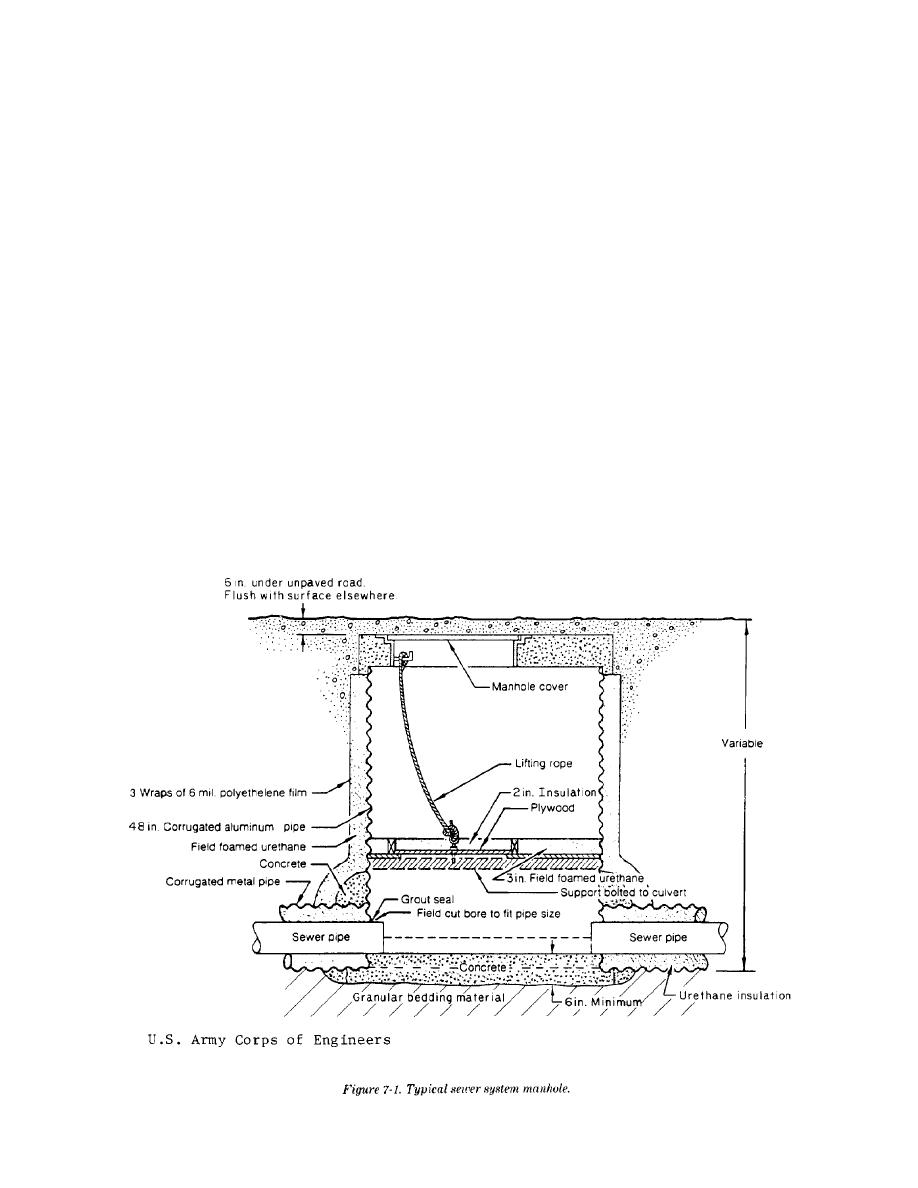
regions. A plastic film wrapped around the outside
in utilidors (chapter 8) can be increased if steam or
of the manhole will be required to prevent bonding
hot water lines are also included in the utility
of the soil to the structure and thereby prevent
package. The thermal design of the sewer piping
damage from frost heaving. Typically, such man-
(chapter 12) must include these wastewater
holes have been insulated with a minimum of 3
temperatures for cost-effectiveness. Storm water
inches of polystyrene or urethane around the out-
will not be admitted to sewers in cold regions. It
side, with a plastic film or other external coating to
lowers the temperature of the wastewater and
prevent moisture damage to the insulation. An insu-
increases the cost of pumping, treatment, and
lated cover will be provided over the wastewater
disposal.
chamber to further reduce heat loss. A firm founda-
b. Pipe materials. The materials selected for
tion is essential, and may require either piling or
sewerage systems will be in accordance with the
excavation, and then sand and gravel backfill. If a
criteria given in TM 5-814-1/AFM 88-11, Vol.1.
poured-in-place concrete invert is used in the man-
Paragraph 6-5 in section 6 of this manual discusses
hole as shown in figure 7-1 and permafrost is at a
the cold climate aspects of these materials.
relatively shallow depth, the concrete will be placed
on insulation board to reduce the downward heat
7-3. Appurtenances.
losses. Spacing of manholes will be in accordance
with TM 5-814-1/AFM 88-11, Vol.1. Solid manhole
These include manholes, cleanouts, building or ser-
covers will be required to prevent entry of surface
vice connections, and flushing siphons.
water.
a. Manholes. Figure 7-1 illustrates typical details
for a buried sewer manhole structure in the cold
7-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
