TM 5-852-4/AFM 88-19, Chap. 4
U. S. Army Corps of Engineers
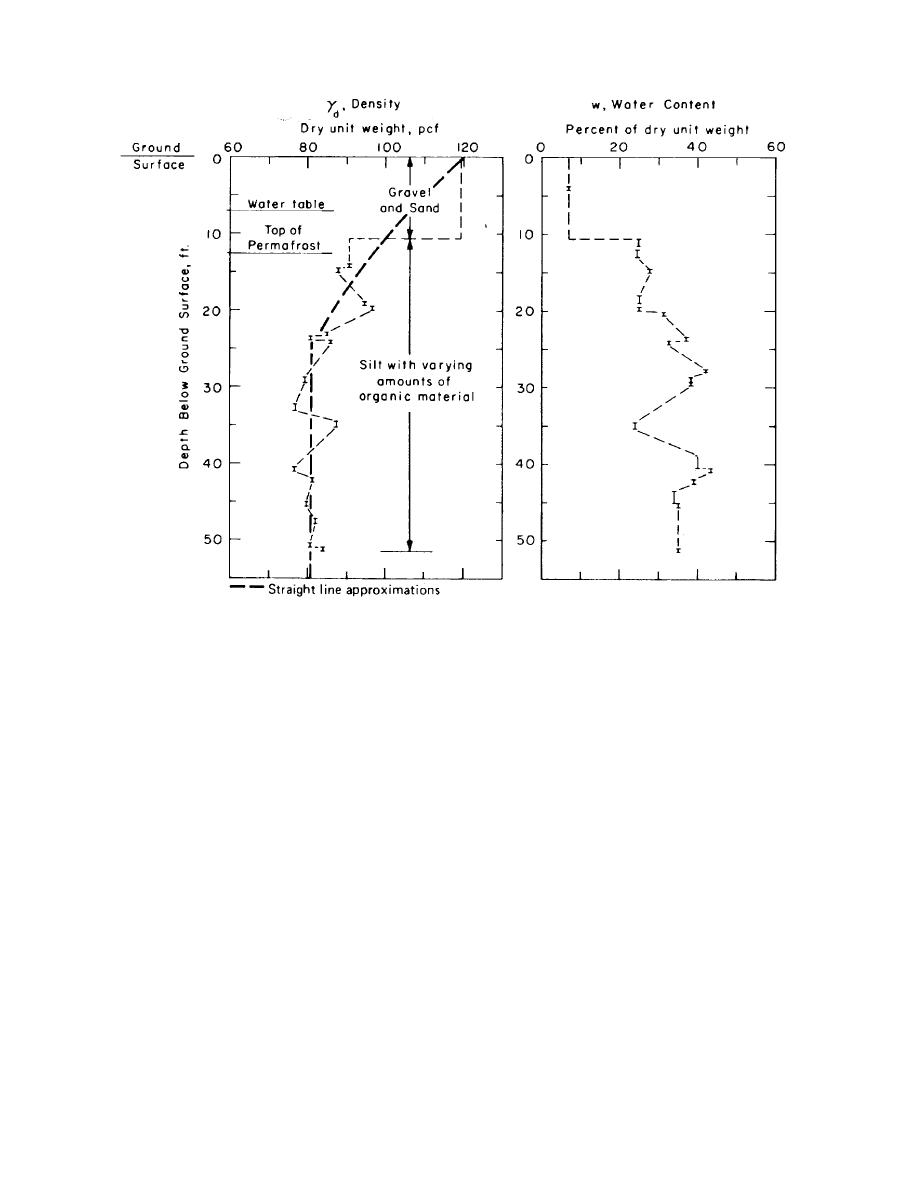
Figure 3-3. Dry density and water content vs. depth for a soil exploration in permafrost.
if it is sufficiently well-trained so that the excess volume
situations, such as where ice is relatively uniformly
of water corresponding to the expansion of water upon
distributed through the soil rather than occurring as
freezing can escape. The top few inches of soil, under
individual ice layers, where clear ice is apparent but there
less than 1 psi of confining pressure, may "fluff" during
still may be direct particle to particle contact in the soil
freezing; this is usually of negligible practical importance
structure, or where swelling rather than reduction in
except to trafficability in the thawing season. However,
volume may occur, thaw consolidation tests would be
135
performed on frozen, undisturbed samples. Crory and
because natural soil may not be completely non-frost-
others have discussed test procedures and analyses.
susceptible and because drainage below the plane of
Two methods of performing such thaw consolidation
freezing may not always be perfect, freezing of upper
tests are available. In one, frozen core samples are
layers of soil may have made them less compact than
trimmed under coldroom conditions to fit a standard soil
underlying materials. This effect may extend as deep as
135
An initial compressive
consolidometer apparatus.
30 feet.
f.
Thaw-consolidation and settlement. When
stress, nominally 1 psi, is applied to the frozen specimen;
it is then allowed to thaw and consolidate (or swell) under
quantitative data are needed on the amount of
this stress to determine the consolidation which is
settlement which will occur on thaw under the foundation
attributable primarily to the ice content of the specimen.
stresses which will exist after construction, rapid
Consolidation is allowed to continue until at least primary
estimates may be made by cumulatively measuring
consolidation is complete. Secondary consolidation may
amounts of ice visible in core samples or in test pit or
rarely have to be taken into account. Successive in-
excavation exposures. If amounts of ice are substantial
these results may be determinative. For less clear-cut
3-7



 Previous Page
Previous Page
