
| Tweet |

Custom Search
|
|

|
||
 MIL-HDBK-1003/13A
2.1.10.2 Concentrating collectors. Concentrating or focusing collectors
intercept direct radiation over a large area and focus it onto a very small
absorber area. These collectors can provide very high temperatures more
efficiently than flat-plate collectors, since the absorption surface area is
much smaller. However, diffuse sky radiation cannot be focused onto the
absorber. Most concentrating collectors require mechanical equipment which
constantly orients the collectors towards the sun and keeps the absorber at
the point of focus.
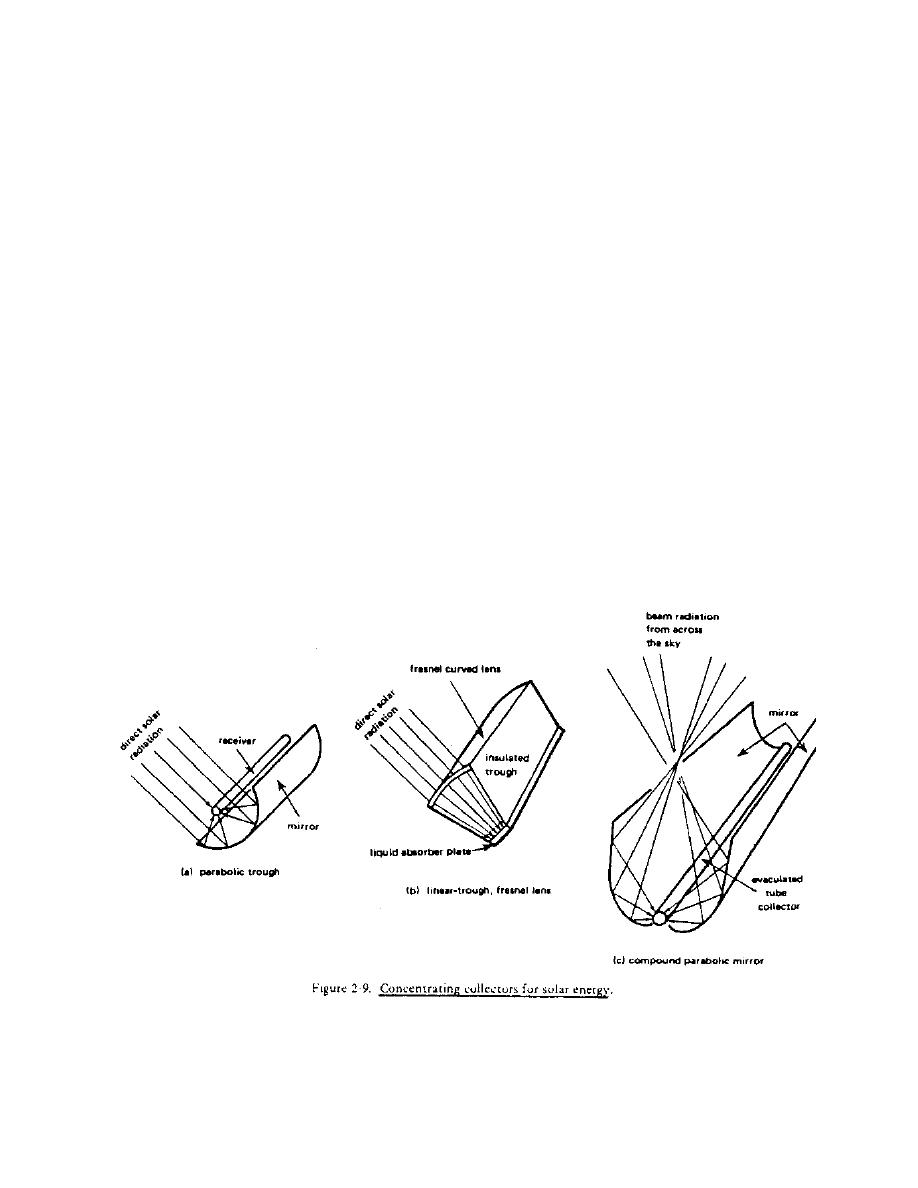
There are many types of concentrating collectors. The most popular types are
the parabolic trough, the linear-trough fresnel lens, and the compound
parabolic mirror. Figure 2-9(a) shows a linear concentrating or parabolic
trough collector. It collects energy by reflecting direct solar radiation
off a large curved mirror and onto a small absorber tube which contains a
flowing heat transfer liquid. The absorber tube is encased in a glass or
metal tube which may or may not be evacuated. This type of collector must
track the sun and can collect only direct radiation.
Figure 2-9(b) shows a linear-trough, fresnel lens collector. In this design
a curved lens is used to focus incoming rays onto a small absorber plate or
tube through which the heat transfer liquid is circulated. This type of
collector also requires a tracking mechanism and can collect only direct
radiation.
Figure 2-9(c) shows a compound parabolic mirror collector. The design of the
mirrors allows the collector to collect and focus both direct and diffuse
radiation without tracking the sun. Periodic changes in the tilt angle are
the only adjustments necessary.
47
|
 |
|
 |
||